Overview of Spinal Injections
Doctors often recommend spinal injections when back or neck problems become severe and unresponsive to conservative treatments. These injections serve two primary purposes: diagnosing the source of pain and providing therapeutic relief.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Uses
- Diagnostic Use: Spinal injections can help identify the exact source of pain in the back, neck, arms, or legs.
- Therapeutic Use: They also alleviate pain, reducing inflammation and discomfort in affected areas.
Most spinal injections are part of a comprehensive treatment program that typically includes exercises to maintain spinal mobility and stability.
Procedure
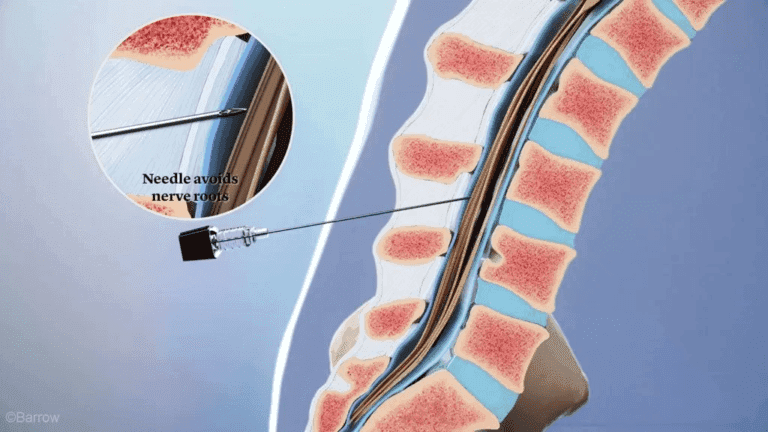
Spinal injections are performed under X-ray guidance, known as fluoroscopy, to ensure accurate medication placement and enhance safety.
The steps involved include:
- Injection of Contrast Dye: A liquid contrast dye is injected before administering the medication.
- Needle Repositioning: If the dye does not flow to the correct location, the needle is repositioned, and more dye is injected until the proper flow is achieved.
- Medication Injection: The therapeutic or diagnostic medication is injected only after confirming the correct flow pattern of the contrast dye.
Types of Spinal Injections
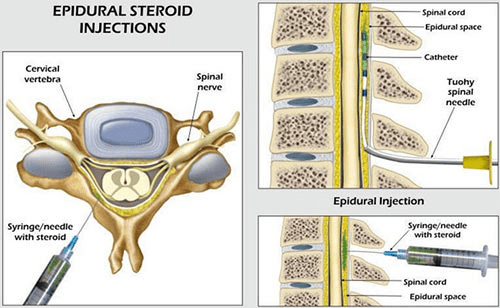
Epidural Injection
Epidural injections are used to treat pain that starts in the spine and radiates to an arm or leg, often caused by inflamed or compressed nerves. These injections can also serve diagnostic purposes.
- Therapeutic Epidural Injections: Involve injecting an anaesthetic and steroid into the epidural space near the affected nerve to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Diagnostic Epidural Injections: Target a specific nerve to determine if it is the source of pain. An immediate response to the injection helps in diagnosing the cause of pain.
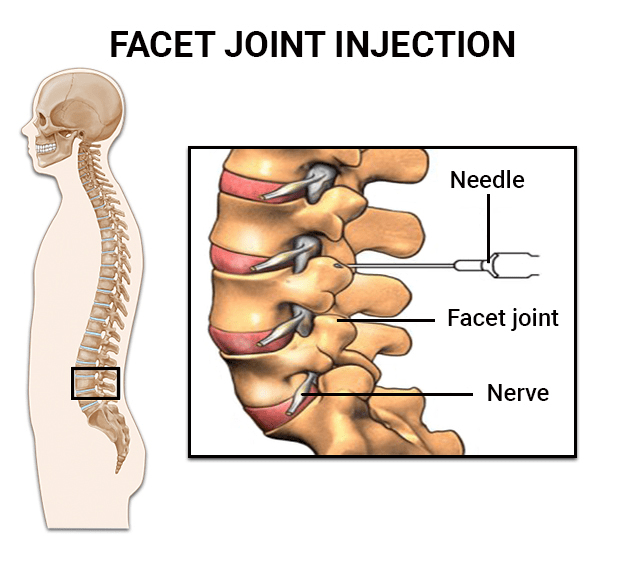
Facet Joint Injection
Facet joint injections are used for diagnostic and therapeutic reasons to treat neck, middle back, or lower back pain.
- Diagnostic Injections: Involve injecting an anaesthetic directly into the joint or anaesthetizing the nerves carrying pain signals away from the joint.
- Therapeutic Injections: May include a steroid to provide long-lasting pain relief. If diagnostic injections indicate a nerve is the pain source, radiofrequency ablation may be used to block pain signals more permanently.
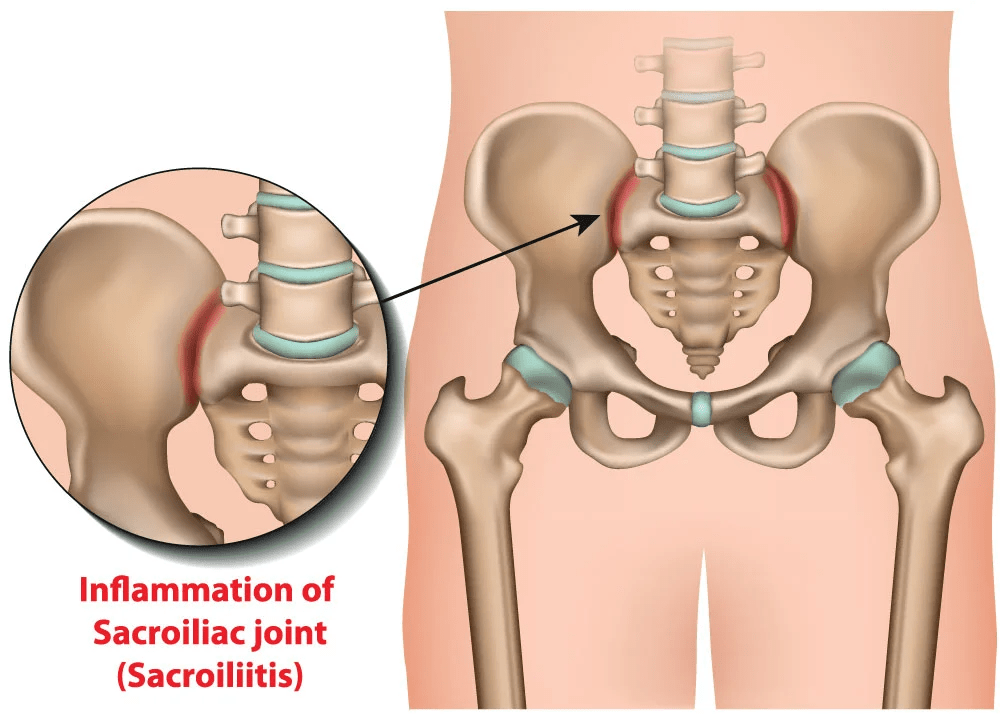
Sacroiliac Joint Injection
Sacroiliac (SI) joint injections target the joints between the sacrum and ilium (pelvic bones), used to diagnose and treat pain in the lower back, buttock, or leg.
- Diagnostic Injections: Anaesthetise the SI joint under X-ray guidance to diagnose SI joint pain.
- Therapeutic Injections: Include a steroid to provide longer-term pain relief.
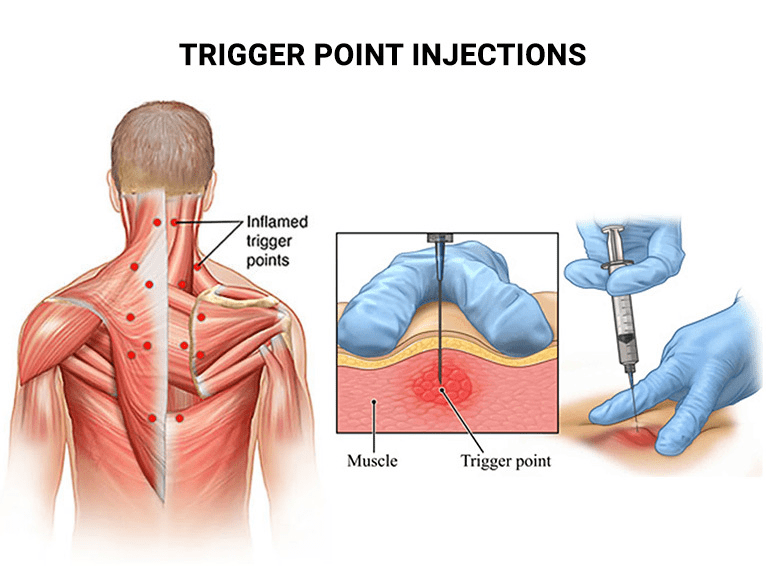
Trigger Point Injection
Trigger point injections treat conditions like fibromyalgia, tension headaches, and myofascial pain syndrome.
- Procedure: This involves injecting a combination of local anaesthetic and steroids into the problem area without requiring X-ray guidance. A similar technique, dry needling, which uses a needle without medication, can be performed in a physical therapy office.
Provocation Discography
Provocation discography is a diagnostic procedure used to identify the source of chronic back pain that has not responded to other treatments.
- Procedure: Involves injecting a liquid into the intervertebral disk’s nucleus pulposus (centre) to stimulate and pressurise it, aiming to reproduce the patient’s pain to identify problematic disks.
Normal Anatomy of the Spine
The spine consists of three segments that form three natural curves when viewed from the side. It plays a crucial role in the overall mechanics and function of the human body.
Complications and Risks
Spinal injection procedures are generally safe, but potential complications include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Nerve Injury
- Arachnoiditis
- Paralysis
- Avascular Necrosis
- Spinal Headache
- Muscle Weakness
- Increased Pain
Common side effects of steroids used in injections include:
- Facial Flushing
- Increased Appetite
- Menstrual Irregularities
- Nausea
- Diarrhoea
- Temporary Increase in Blood Sugar
Contraindications
Certain conditions may make individuals unsuitable candidates for spinal injections, such as:
- Skin Infection at Injection Site
- Bleeding Disorders or Anticoagulation Therapy
- Uncontrolled High Blood Pressure or Diabetes
- Allergy to Contrast, Anesthetics, or Steroids