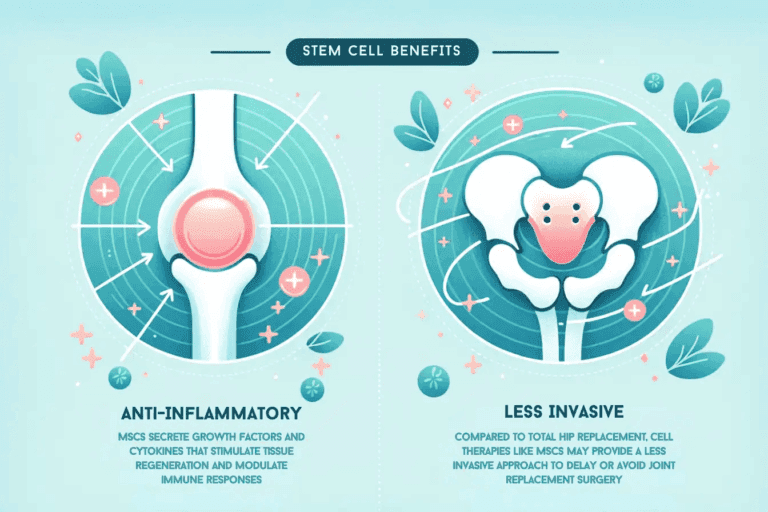
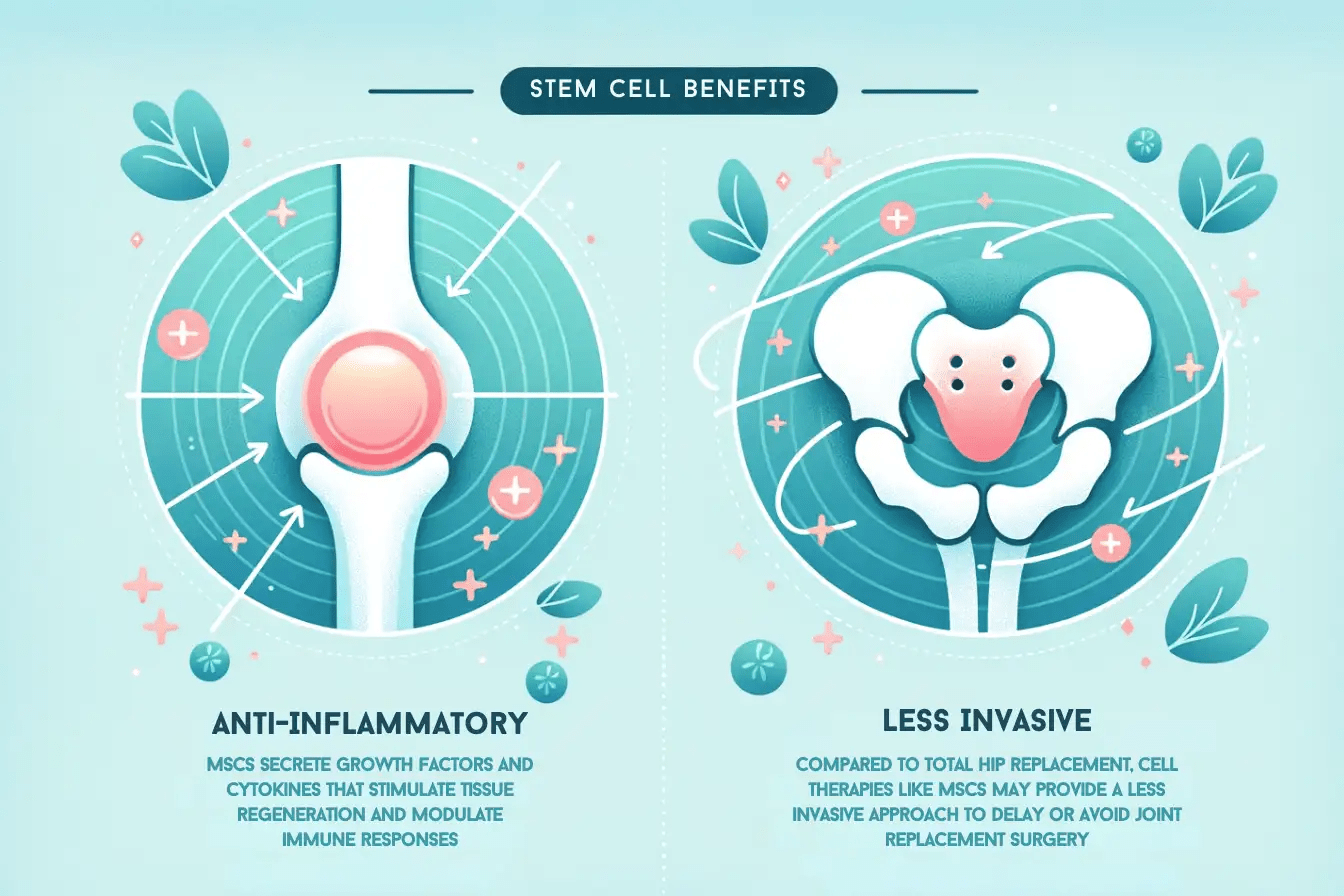
The Promise of Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine in hip preservation:
- Utilises stem cell therapy, platelet-rich plasma (PRP), and growth factor injections
Benefits:
- Promotes tissue repair and regeneration within the hip joint
- Reduces pain associated with hip conditions
Stem cell therapy:
- Stem cells can differentiate into cartilage and bone cells
- It offers the potential for regenerating damaged hip structures
PRP therapy:
- Harnesses healing properties of platelets from the patient’s blood
- Accelerates healing and tissue repair mechanisms in the hip joint
Growth factor injections:
- Delivers specific growth factors directly to the site of hip injury
- Stimulates cellular responses for tissue regeneration and repair
Clinical evidence:
- Demonstrates improved hip function and reduced pain in patients
- Validates the efficacy of regenerative medicine in hip preservation
Potential to transform hip preservation:
- Offers minimally invasive, biologic alternatives to traditional surgeries
- Provides personalised treatments for various hip conditions, enhancing long-term hip health
Combining Techniques for Optimal Results: Maximising Hip Preservation
Synergies between Minimally Invasive Surgery and Regenerative Medicine:
- Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) focuses on precise interventions with minimal tissue damage.
- Regenerative medicine aims to promote tissue repair and regeneration using biologic therapies.
- Combined, these techniques offer complementary approaches to hip preservation.
Enhancing Outcomes and Improving Patient Recovery:
- Minimally invasive surgery reduces surgical trauma, leading to faster recovery times.
- Regenerative medicine accelerates tissue healing and promotes long-term joint health.
- Together, they can optimise outcomes by addressing both structural and biological aspects of hip pathology.
Advances in Technology and Surgical Approaches:
- Technological innovations allow for minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision.
- Integrating regenerative medicine techniques, such as stem cell therapy or PRP injections, into minimally invasive procedures is becoming increasingly feasible.
- Surgeons can now tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs, maximising the benefits of combined approaches.
Challenges and Future Directions in Hip Preservation Techniques
Identification of Challenges and Limitations:
- Limited accessibility and expertise: Not all healthcare facilities may have access to advanced minimally invasive surgical techniques or regenerative medicine therapies, leading to disparities in patient care.
- Cost implications: The initial investment in equipment and training for minimally invasive surgery and regenerative medicine may pose financial challenges for healthcare institutions.
- Long-term efficacy: While minimally invasive surgery and regenerative medicine show promise, long-term outcomes and durability of these techniques require further investigation.
- Patient selection: Identifying the most suitable candidates for these advanced techniques remains challenging, particularly in cases with complex hip pathologies or comorbidities.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions:
- Emerging technologies: Continued advancements in imaging modalities, surgical instruments, and biologic therapies are expected to refine minimally invasive surgery and regenerative medicine for hip preservation.
- Personalised medicine: Research is focused on developing customised treatment approaches based on patient-specific factors such as age, activity level, and underlying hip pathology.
- Novel treatment modalities: Researchers are exploring novel regenerative medicine approaches, such as tissue engineering and gene therapy, to enhance tissue repair and regeneration in the hip joint.
- Clinical trials: Ongoing clinical trials evaluate the safety and efficacy of combined minimally invasive surgery and regenerative medicine techniques, providing valuable insights into their potential benefits and limitations.
Consideration of Impact on Healthcare Costs and Patient Outcomes:
- Cost-effectiveness: While the initial costs of minimally invasive surgery and regenerative medicine may be higher, studies suggest that they may lead to reduced healthcare utilisation and lower overall costs in the long term due to shorter hospital stays and faster recovery times.
- Patient-reported outcomes: Improvements in patient-reported outcomes, such as pain relief, functional status, and quality of life, are essential considerations in assessing the value of hip preservation techniques.
- Health economics research: Future studies should explore the cost-effectiveness of minimally invasive surgery and regenerative medicine compared to traditional surgical approaches, taking into account both direct healthcare costs and indirect societal costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, integrating minimally invasive surgery and regenerative medicine in hip preservation signifies a pivotal advancement in modern orthopaedics, offering patients less invasive alternatives with superior outcomes. By synergizing these techniques, healthcare providers can optimise patient recovery and enhance hip function, improving overall quality of life. Ongoing research and technological advancements will continue to drive innovation in hip preservation, addressing challenges and further refining treatment modalities to maximise patient outcomes while considering the economic impact on healthcare systems.