Swelling is a common and natural response to injury, and while it plays a role in healing, excessive or prolonged swelling can hinder recovery. This article provides a comprehensive overview of effective strategies to reduce arm swelling after an injury, ensuring a smoother and faster healing process.
Understanding Swelling: Causes and Phases
What is Swelling?
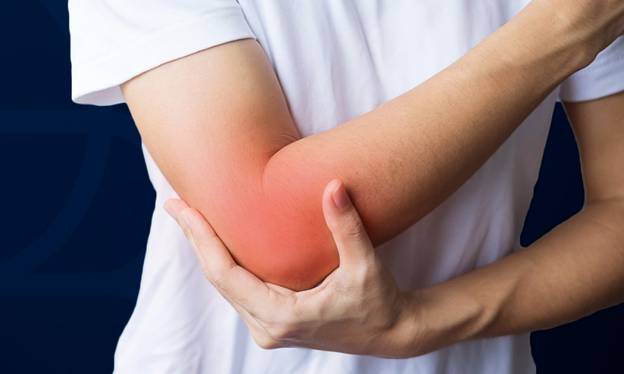
Swelling, or edema, occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues of the affected area. This is part of the body’s inflammatory response to injury, where increased blood flow brings essential nutrients and immune cells to the site to aid in healing.
Phases of Swelling:
- Acute Swelling: This usually occurs within the first 48-72 hours after an injury. The swelling peaks and begins to subside as the body starts to heal.
- Subacute Swelling: This phase can last up to 2-3 weeks, with gradual improvement.
- Chronic Swelling: If swelling persists beyond three weeks, it may indicate complications, requiring medical evaluation.
Top Tips for Reducing Arm Swelling
1. Rest and Immobilization
Resting the injured arm is crucial to avoid further damage. Immobilization using slings or splints can help stabilize the area, preventing unnecessary movement that could exacerbate swelling.
2. Ice Application
Applying ice is most effective within the first 24-48 hours. Ice helps reduce swelling by constricting blood vessels and limiting fluid accumulation. Use an ice pack wrapped in a thin cloth for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours.
3. Elevation
Elevating the injured arm above heart level uses gravity to assist in draining excess fluid away from the swollen area. This technique is particularly effective when combined with ice application.
4. Compression
Compression wraps or sleeves can prevent fluid build-up by applying consistent pressure on the injured area. Compression also helps to maintain proper circulation, reducing the duration of swelling.
5. Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
MLD is a specialized massage technique that encourages the flow of lymphatic fluid away from the swollen area. This technique can be performed by a trained therapist or at home with gentle, upward strokes towards the heart.
6. Hydration
Staying hydrated may seem counterintuitive, but it’s essential. Proper hydration helps to reduce fluid retention by maintaining balance in the body’s systems. Dehydration can cause the body to hold onto fluid, worsening swelling.
7. Diaphragmatic Breathing
Deep breathing exercises can stimulate the lymphatic system, aiding in the removal of excess fluid. This technique is particularly effective for swelling that persists beyond the initial phase of healing.
8. Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Non-prescription anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen can help reduce swelling and manage pain. However, these should be used cautiously and under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
9. Exercise and Gentle Movement
While rest is crucial, gentle movement and specific exercises prescribed by a physical therapist can help reduce swelling. Movement helps stimulate blood flow, preventing stiffness and further complications.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If swelling does not improve within a few days, or if it worsens, it’s essential to seek medical advice. Additionally, if swelling is accompanied by severe pain, redness, or warmth, these could be signs of infection or other complications requiring immediate medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long should swelling last after an arm injury?
Swelling typically peaks within 48-72 hours and gradually subsides over 1-2 weeks. If it persists beyond three weeks, it may be considered chronic and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. - Can I apply heat to reduce swelling?
Heat is generally not recommended during the acute phase (first 48 hours) as it can increase swelling. However, after the initial phase, alternating heat and ice can sometimes be beneficial to promote healing. - Is it normal for the swelling to come and go?
Yes, fluctuations in swelling are common, especially with changes in activity levels. However, consistent or worsening swelling should be assessed by a healthcare professional. - What is the best sleeping position to reduce arm swelling?
Elevate the injured arm on a pillow above heart level while sleeping to promote fluid drainage and reduce swelling. - Can diet affect swelling?
Yes, a diet high in salt can contribute to fluid retention, worsening swelling. Reducing salt intake and staying hydrated can help manage swelling.
By following these tips and understanding when to seek medical advice, you can effectively manage and reduce arm swelling after an injury, leading to a smoother and more efficient recovery.
For further personalized advice, always consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist, especially if the swelling persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms.