Introduction
Repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) are a group of musculoskeletal conditions that arise from overuse of specific muscle groups, tendons, and nerves due to repetitive motion. These injuries are commonly associated with activities that involve continuous, repetitive motion of the arm, such as typing, manual labor, or sports. In this article, we will delve into the impact of repetitive strain injuries on arm health, exploring the causes, symptoms, prevention strategies, and treatment options available. Additionally, we will answer some of the most frequently asked questions related to RSIs.
Chapter 1: Understanding Repetitive Strain Injuries
What Are Repetitive Strain Injuries?
Repetitive strain injuries (RSIs) are conditions that affect the musculoskeletal and nervous systems, primarily due to repetitive motions, forceful exertions, vibrations, mechanical compression, or sustained or awkward positions. These injuries often affect the upper body, particularly the arms, wrists, and hands.
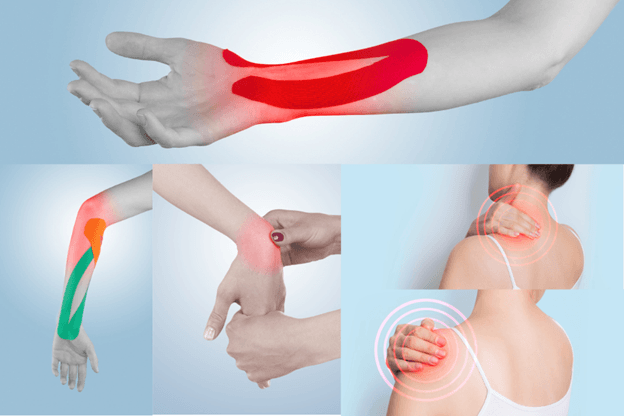
Types of Repetitive Strain Injuries in the Arm
RSIs encompass various conditions, including:
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of a tendon, commonly affecting the elbow or wrist.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the median nerve in the wrist.
- Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis): Inflammation of the tendons on the outside of the elbow.
- Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis): Inflammation of the tendons on the inside of the elbow.
- De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis: Inflammation of the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion bones and muscles.
- Rotator Cuff Syndrome: Inflammation or tears in the tendons and muscles around the shoulder joint.
Causes of Repetitive Strain Injuries
RSIs in the arm are typically caused by:
- Repetitive Motion: Continuous movements, such as typing, lifting, or using tools.
- Overuse: Performing an activity too often without adequate rest.
- Poor Posture: Maintaining an awkward or unnatural position for extended periods.
- Insufficient Ergonomics: Working environments that do not support proper posture and movement.
- Vibration: Prolonged exposure to vibrating tools or machinery.
- Cold Environments: Working in cold conditions without proper protection.
Chapter 2: Symptoms and Diagnosis of Repetitive Strain Injuries
Common Symptoms of RSIs in the Arm
The symptoms of RSIs can vary depending on the specific condition but generally include:
- Pain: Aching, throbbing, or burning pain in the affected area.
- Weakness: Reduced strength or difficulty in gripping or lifting.
- Numbness or Tingling: Sensations of pins and needles, particularly in the hands or fingers.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the affected joint or limb.
- Swelling: Inflammation in the affected area.
- Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the joint or limb through its full range of motion.
How Are RSIs Diagnosed?
Diagnosing RSIs typically involves:
- Medical History: Discussing symptoms, activities, and any history of similar issues.
- Physical Examination: Checking the range of motion, strength, and any signs of inflammation or tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds may be used to assess damage to bones, tendons, or nerves.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: Used to diagnose conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome by assessing nerve function.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience persistent pain, numbness, or weakness in your arm, it is important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and intervention can prevent further damage and improve recovery outcomes.
Chapter 3: The Impact of RSIs on Arm Health
Short-Term Impact of RSIs
In the short term, RSIs can lead to:
- Pain and Discomfort: Making it difficult to perform daily tasks or work-related activities.
- Reduced Productivity: Due to pain, weakness, or limited range of motion.
- Increased Absenteeism: Time off work to manage symptoms or attend medical appointments.
Long-Term Impact of RSIs
If left untreated, RSIs can have significant long-term consequences:
- Chronic Pain: Persistent pain that can be difficult to manage.
- Permanent Damage: Long-term inflammation or nerve compression can lead to irreversible damage.
- Disability: Severe cases of RSIs can result in permanent loss of function, requiring changes in employment or lifestyle.
- Mental Health Impact: Chronic pain and disability can contribute to anxiety, depression, and reduced quality of life.
Impact on Specific Populations
Certain groups are more susceptible to RSIs, including:
- Office Workers: Those who spend long hours typing or using a computer.
- Manual Laborers: Individuals who engage in repetitive physical tasks, such as construction workers or assembly line workers.
- Athletes: Especially those involved in sports requiring repetitive arm motions, such as tennis or golf.
- Older Adults: As tendons and muscles lose flexibility with age, the risk of RSIs increases.
Chapter 4: Prevention of Repetitive Strain Injuries
Ergonomics in the Workplace
Creating an ergonomic work environment can significantly reduce the risk of RSIs. Key strategies include:
- Proper Chair and Desk Height: Ensuring that your chair and desk are at the correct height to avoid strain on your arms and shoulders.
- Keyboard and Mouse Positioning: Keeping your wrists straight and your hands at or below elbow level.
- Frequent Breaks: Taking regular breaks to stretch and move, reducing the risk of overuse injuries.
- Ergonomic Equipment: Using tools and devices designed to reduce strain, such as ergonomic keyboards or mouse pads.
Exercises and Stretching
Incorporating stretching and strengthening exercises into your daily routine can help prevent RSIs:
- Wrist Stretches: Stretching the flexor and extensor muscles of the wrist.
- Forearm Strengthening: Exercises to build strength in the forearm muscles.
- Shoulder Mobility: Exercises to maintain range of motion and flexibility in the shoulder joint.
- Posture Training: Techniques to improve posture and reduce strain on the arms and shoulders.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can also help prevent RSIs:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can reduce the risk of inflammation.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring sufficient sleep and rest periods to allow the body to recover from repetitive activities.
- Stress Management: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, as stress can contribute to muscle tension and increase the risk of RSIs.
Chapter 5: Treatment Options for Repetitive Strain Injuries
Conservative Treatments
Initial treatment for RSIs often involves conservative measures:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms to allow the affected area to heal.
- Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice to reduce inflammation and heat to relieve stiffness.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen to manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can develop a tailored exercise program to improve strength and flexibility.
Medical Interventions
If conservative treatments are not effective, medical interventions may be necessary:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections to reduce inflammation in the affected area.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to repair damaged tendons or nerves.
- Orthotics and Braces: Devices to support and immobilize the affected area, reducing strain and allowing healing.
Alternative Therapies
Some individuals may find relief through alternative therapies:
- Acupuncture: Targeting specific points to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Massage Therapy: Techniques to reduce muscle tension and improve circulation.
- Chiropractic Care: Adjustments to improve joint function and reduce strain on the musculoskeletal system.
Chapter 6: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the most common causes of RSIs in the arm?
Repetitive motion, overuse, poor ergonomics, and prolonged static positions are the most common causes of RSIs in the arm. Activities such as typing, using tools, and certain sports can contribute to these injuries.
How can I prevent RSIs if I work at a computer all day?
To prevent RSIs, ensure your workspace is ergonomically designed, take regular breaks to stretch, and perform exercises that strengthen the muscles in your arms, shoulders, and back.
Can RSIs be cured completely?
While many RSIs can be managed effectively with treatment, complete recovery depends on the severity of the injury, the duration of symptoms, and adherence to treatment and prevention strategies.
What are the signs that I should see a doctor for RSI symptoms?
If you experience persistent pain, numbness, or weakness in your arm that does not improve with rest, or if you have difficulty performing daily tasks, it is important to seek medical attention.
Are there specific exercises that can help prevent RSIs?
Yes, exercises that focus on stretching and strengthening the muscles and tendons in the arms, shoulders, and back can help prevent RSIs. Consult a physical therapist for a tailored exercise program.
How long does it take to recover from an RSI?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment approach. Some individuals may recover in a few weeks, while others may take several months.
Can RSIs lead to permanent damage?
If left untreated, RSIs can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and in severe cases, permanent damage or disability.
Are there any long-term effects of RSIs on arm health?
Long-term effects of untreated RSIs include chronic pain, reduced function, and the potential for developing other musculoskeletal disorders.
Is surgery always required for treating RSIs?
Surgery is usually considered a last resort when conservative treatments fail to alleviate symptoms or if there is significant damage to the tendons or nerves.
Can lifestyle changes help in managing RSIs?
Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, reducing stress, and ensuring adequate rest can help manage and prevent RSIs.
Conclusion
Repetitive strain injuries can have a significant impact on arm health, affecting not only physical function but also overall quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for RSIs, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent these injuries and maintain arm health. If you suspect you may have an RSI, it is crucial to seek medical advice early to prevent long-term complications.