Introduction:
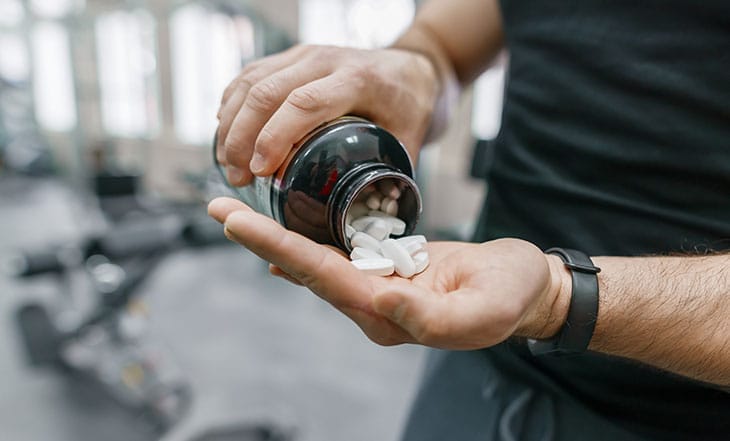
Creatine supplements have garnered popularity among athletes, with many seeking an edge in performance enhancement. Among the most widely used sports supplements, creatine is believed by some athletes, including children and adolescents, to boost strength and athletic performance.
Despite its widespread use, the evidence supporting the efficacy of creatine supplements in enhancing sports performance still needs to be conclusive.
Moreover, there needs to be more research on the potential long-term health implications of creatine supplementation, particularly among adolescents and children still undergoing growth and development.
Due to these uncertainties surrounding its effects, caution is warranted, especially for young individuals.
As such, it is recommended that children and adolescents refrain from taking creatine supplements until further research elucidates its safety and efficacy profiles.
Understanding Creatine:
Creatine is a natural energy source crucial for muscle function, primarily produced in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas.
While meat and fish intake can supplement creatine levels, vegetarians may have lower amounts due to dietary restrictions. Predominantly stored in skeletal muscles, creatine fuels physical activity, with additional usage in vital organs like the heart and brain.
Supplementation with creatine may elevate muscle creatine levels, potentially enhancing energy production and accelerating energy generation during exertion.
Combining creatine supplements with training regimens can enhance performance by providing rapid bursts of energy, which is particularly beneficial for activities such as sprinting and weightlifting.
Individuals with lower natural creatine levels, including vegetarians, may experience more pronounced effects from creatine supplementation.
However, a threshold may exist known as the “saturation point,” limiting the muscles’ capacity to store creatine.
Accessible and Widely Used:
Creatine supplements are readily available under various brand names and formulations and are easily found over the counter at vitamin shops, pharmacies, grocery stores, and online platforms.
The usage of creatine supplements is pervasive and is anticipated to continue increasing. Professional sports associations, which include the International Olympic Committee and (NCAA ) the National Collegiate Athletic Association ), do not prohibit their use.
Predominantly, creatine supplement users are:
- Male
- Engaged in power sports like football, wrestling, hockey, and bodybuilding
- Athletes across all performance levels, from professionals to amateurs, including college, high school, and even middle school athletes.
Research indicates a growing trend of adolescents, particularly those focused on athletics and appearance, turning to performance-enhancing supplements like creatine. A study by the American Academy of Pediatrics surveyed middle and high school students aged 10 to 18, revealing creatine use across all grades, with approximately 5.6% of participants admitting to its use and a significant 44% of high school senior athletes reporting creatine consumption.
Supplement Safety Considerations:
While creatine is derived from natural sources, its supplementation may not always be safe.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate nutritional supplements. Consequently, creatine products available on the market may vary in potency and quality, lacking guaranteed safety or purity standards.
According to research from the Mayo Clinic, many young athletes who use creatine supplements often rely on peer advice rather than seeking guidance from healthcare professionals. Moreover, some users may not be aware of appropriate dosages, leading to potential overconsumption.
Side Effects of Creatine Use:
- Creatine supplementation may cause water retention in muscles, leading to potential weight gain.
- Long-term use of creatine supplements can result in various side effects, including muscle cramps, dehydration, diarrhoea, nausea, and in severe cases, seizures.
- Specific circumstances, such as dehydration during activities like wrestling, can increase the risks associated with creatine supplementation.
- Dehydration combined with creatine intake may exacerbate fluid retention effects, potentially leading to further complications.
- Individuals aiming to lose weight should exercise caution with creatine supplementation, as it may hinder weight loss efforts due to water retention.
- While creatine can enhance exercise performance, its potential side effects should be considered carefully, especially in situations where dehydration or weight loss goals are involved.
Understanding Potential Health Risks
Medical experts are yet to fully comprehend the potential effects of creatine supplements on vital organ systems like the heart, brain, kidneys, liver, and reproductive organs. Additionally, there needs to be more understanding regarding the interactions between creatine supplements and other substances like over-the-counter medications, prescription drugs, vitamins, and energy drinks.
Ongoing medical research aims to shed light on the safety and efficacy of creatine supplements.
Researchers are exploring whether creatine supplementation could offer therapeutic benefits in conditions characterised by muscle deterioration, such as heart disease, neuromuscular disorders, and stroke.
Despite ongoing research, the long-term health implications of creatine supplementation still need to be discovered, particularly in growing children and adolescents.
Consequently, individuals under the age of 18, as well as pregnant or nursing women, are strongly advised against the use of creatine supplements. Furthermore, kidney disease patients should abstain from creatine supplementation due to potential risks.
Regardless of age or health status, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before considering using creatine supplements. Seeking medical advice ensures informed decision-making and mitigates potential risks associated with supplementation.
Summary:
Creatine supplementation is a common practice among athletes, but its long-term health effects and interactions with other substances are not fully understood. Concerns include potential impacts on organs and unknown interactions with medications. Research is ongoing, particularly for treating muscle-related conditions, but caution is advised, especially for certain groups like children, pregnant women, and those with kidney issues. Consulting a healthcare professional before starting creatine supplements is essential to minimise risks.