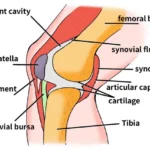
Orthopaedic surgery is a medical specialty focused on diagnosing, treating, and preventing conditions affecting the musculoskeletal system. This system includes bones, muscles, joints, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and other soft tissues. These surgeries help maintain or restore the function and mobility of the body.
Types of Orthopaedic Surgery
Orthopaedic surgeons may specialise in different areas of the musculoskeletal system, focusing on the following:
- Hip and Knee: Including hip replacements and knee replacements.
- Hand and Wrist: Such as carpal tunnel release and tendon repairs.
- Foot and Ankle: Including surgeries for bunions and Achilles tendon repairs.
- Spine: Spinal fusions and disc surgeries.
- Shoulder and Elbow: Rotator cuff repairs and elbow arthroscopy.
- Oncology: Treatment of bone tumours.
- Trauma: Repair of fractures and severe injuries.
- Sports Medicine: ACL repairs and other sports-related injuries.
- Paediatric Orthopaedics: Treating children with musculoskeletal issues.
Conditions Treated by Orthopaedic Surgery
Orthopaedic surgery addresses various conditions, including:
- Joint, muscle, and bone pain.
- Muscle, cartilage, or ligament tears.
- Fractures and breaks.
- Arthritis.
- Bursitis.
- Bone tumors.
- Congenital deformities.
Prevalence of Orthopaedic Surgery in the UK
Orthopaedic surgery is common in the UK, with procedures such as knee replacements and hip replacements being among the most frequently performed surgeries.
Before Orthopaedic Surgery
Before surgery, patients will meet with an orthopaedic surgeon for a consultation. The surgeon will take a complete medical history, perform a physical examination, and review any necessary imaging tests like X-rays. This evaluation helps determine the best course of action and prepare for the surgery.
The Surgical Procedure
On the day of surgery, patients are prepared in a hospital setting. An anaesthetist administers anaesthesia to ensure the patient is comfortable and pain-free during the procedure. The specific steps of the surgery depend on the type of operation being performed, whether it involves repairing a fracture, reconstructing a ligament, or replacing a joint.
Post-Surgery Care
After the surgery, patients are moved to a recovery area until the anaesthesia wears off. Depending on the procedure, patients may either go home the same day or stay in the hospital overnight. Post-surgery care includes instructions on how to care for the surgical site, manage pain, and what activities to avoid during recovery.
Recovery Time
Recovery times vary depending on the type of surgery:
- ACL surgery: Approximately nine months.
- Bone fracture surgery: Around three months.
- Knee replacement: Roughly three months.
Patients will have follow-up appointments to monitor their recovery and may require physical therapy to regain strength and mobility.
Risks and Benefits
Benefits:
- Pain reduction.
- Improved function and mobility.
- Corrected deformities.
- Removal of tumours.
Risks:
- Bleeding.
- Infection.
- Joint pain or stiffness.
- Blood clots.
- Muscle weakness.
- Numbness.
When to Contact a Doctor
Patients should contact their healthcare provider if they experience:
- Fever.
- Swelling.
- Changes in skin colour.
- Severe pain.
- Fluid or blood draining from the incision.
Regular follow-up appointments will help ensure proper recovery.
Conclusion
Orthopaedic surgery plays a vital role in treating and managing conditions that affect the musculoskeletal system. By understanding the procedures, benefits, and risks, patients can make informed decisions about their healthcare. For more information on orthopaedic surgery and to consult with a specialist, visit your local NHS services or private healthcare providers in the UK.