Understanding Golfer’s Elbow
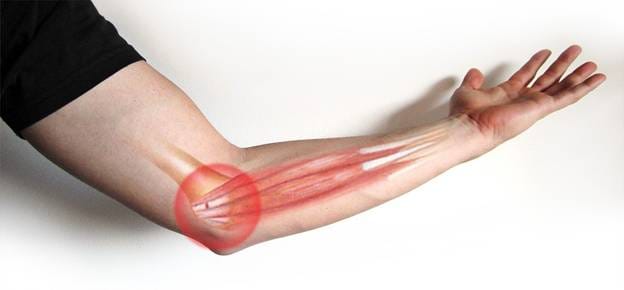
Golfer’s elbow, medically known as medial epicondylitis, is a condition characterized by pain and inflammation on the inner side of the elbow, where the tendons of the forearm muscles attach to the bony bump on the inside of the elbow. Despite its name, golfer’s elbow is not exclusive to golfers and can affect anyone who performs repetitive arm and wrist motions.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of golfer’s elbow include:
- Pain and tenderness: Usually felt on the inner side of the elbow and sometimes extending along the inner side of the forearm.
- Stiffness: The elbow may feel stiff, and making a fist can hurt.
- Weakness: There may be weakness in the hands and wrists.
- Numbness or tingling: These sensations might radiate into one or more fingers (usually the ring and little fingers).
Causes
Golfer’s elbow is caused by damage to the muscles and tendons that control the wrist and fingers. Repetitive stress, particularly from gripping, flexing, or swinging, can lead to small tears in the tendons. Common activities that can lead to golfer’s elbow include:
- Sports like golf, tennis, and baseball.
- Weight training, particularly improper lifting techniques.
- Jobs that involve repetitive motions, such as carpentry or typing.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination where the doctor assesses pain and tenderness in the elbow. They may also ask you to perform specific movements to pinpoint the pain source. Imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans, might be used to rule out other conditions.
Treatment
Treatment for golfer’s elbow aims to reduce pain and inflammation, promote healing, and prevent recurrence. Here are common treatment methods:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoid activities that exacerbate the pain. Resting the elbow is crucial for recovery.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to stretch and strengthen the forearm muscles and tendons. Techniques may include:
- Stretching exercises: To improve flexibility.
- Strengthening exercises: To build endurance in the forearm muscles.
- Manual therapy: Techniques to relieve muscle tension and improve blood flow.
- Bracing: Wearing a counterforce brace on the forearm can reduce tendon strain and alleviate pain.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, steroid injections might be used to reduce inflammation.
- Shock Wave Therapy: This non-invasive treatment uses sound waves to stimulate healing in the affected tendons.
- Surgery: Rarely, if conservative treatments fail and the condition is severe, surgery might be needed to remove damaged tissue.
Prevention
Preventing golfer’s elbow involves:
- Proper Technique: Ensure correct technique in sports and activities to avoid undue stress on the elbow.
- Strengthening and Stretching: Regularly perform exercises to strengthen and stretch the forearm muscles.
- Equipment Check: Ensure sports equipment is properly sized and maintained.
- Warm-Up: Always warm up before engaging in any physical activity.
FAQs
Q: How long does it take to recover from golfer’s elbow? A: Recovery time varies, but with appropriate treatment, most people recover within a few weeks to several months.
Q: Can golfer’s elbow heal on its own? A: Minor cases may improve with rest and conservative treatment. Persistent or severe cases might require medical intervention.
Q: Is it necessary to stop all activities if I have golfer’s elbow? A: It’s important to avoid activities that exacerbate pain, but complete rest isn’t always necessary. Modify activities to reduce stress on the elbow.
Q: Can golfer’s elbow become chronic? A: If not properly treated, golfer’s elbow can become a chronic issue, leading to long-term pain and discomfort.