Introduction
Arm injuries are common in many sports, particularly those involving repetitive motions or high-impact activities. Preventing these injuries is critical for maintaining athlete performance and long-term joint health. This article will cover key strategies for preventing arm injuries, focusing on evidence-based practices that can be applied across various sports disciplines.
Understanding Arm Injuries in Sports
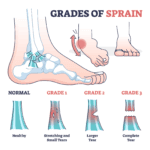
Arm injuries can result from acute trauma, such as falls or collisions, or from chronic overuse, such as repetitive throwing or swinging motions. Common injuries include strains, sprains, tendinitis, and fractures. Overuse injuries are particularly prevalent and often occur when athletes exceed their physical limits without adequate rest or conditioning.
Key Prevention Strategies
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down:
A proper warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles, making them more flexible and less prone to injury. This can include dynamic stretching, light cardio, and sport-specific drills. Similarly, cooling down with static stretching helps reduce muscle stiffness and aids in recovery. - Strength Training and Conditioning:
Strengthening the muscles surrounding the shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints is crucial. This not only improves joint stability but also enhances overall arm strength and endurance. Conditioning should be progressive, gradually increasing the intensity to avoid overloading the muscles and tendons. - Proper Technique:
Ensuring that athletes use the correct techniques for their sport is vital in preventing injuries. Coaches and trainers should emphasize the importance of biomechanics, particularly in sports like baseball, tennis, and swimming, where improper technique can lead to repetitive stress injuries. - Rest and Recovery:
Adequate rest between training sessions allows muscles and tendons to recover, reducing the risk of overuse injuries. Incorporating rest days and using periodization in training programs can help manage workload and prevent burnout. - Use of Protective Gear:
In contact sports, wearing protective gear such as pads and braces can reduce the risk of acute injuries. For example, elbow pads can protect against fractures and contusions in sports like hockey or skateboarding. - Regular Medical Check-Ups:
Routine evaluations by a sports physician can help detect early signs of overuse injuries and other potential issues. Early intervention can prevent minor issues from becoming serious injuries. - Education and Awareness:
Athletes should be educated on the signs of overuse injuries, such as persistent pain or decreased performance, and encouraged to seek medical advice early. Awareness programs can also be beneficial in promoting injury prevention practices among sports teams.
Special Considerations for Different Sports
Each sport presents unique challenges and risks for arm injuries. For example:
- Baseball and Softball: Emphasize shoulder and elbow conditioning and limit the number of pitches thrown.
- Tennis: Focus on wrist and forearm strengthening, and ensure proper racquet grip and swing technique.
- Swimming: Include exercises that enhance shoulder stability and flexibility to prevent rotator cuff injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How can athletes differentiate between normal soreness and a potential injury?
Mild soreness after exercise is normal and typically resolves within a day or two. However, sharp, persistent pain or swelling that worsens with activity may indicate an injury that requires medical evaluation. - Is it safe to continue training if an athlete experiences mild pain?
Continuing to train through mild pain can lead to more severe injuries. It’s crucial to assess the cause of the pain and modify training accordingly. Rest and appropriate treatment should be prioritized. - What role do nutrition and hydration play in injury prevention?
Proper nutrition and hydration are essential for muscle function and recovery. Adequate intake of proteins, vitamins, and minerals supports tissue repair, while staying hydrated helps maintain muscle elasticity and joint lubrication.
By following these strategies, athletes and coaches can significantly reduce the risk of arm injuries and ensure a safer, more effective training environment.