Introduction
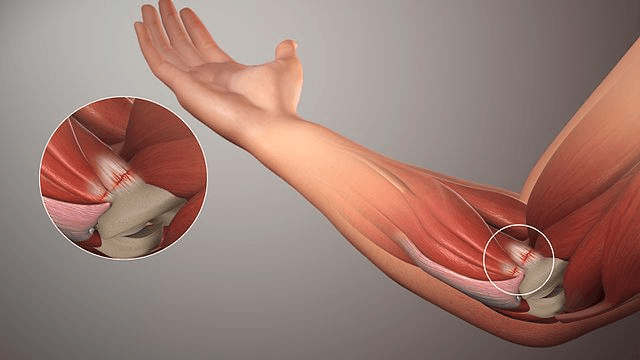
Bicep tendonitis, also known as biceps tendinitis, is a common condition characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendons connecting the biceps muscle to the shoulder and elbow. This condition often results from repetitive motion or overuse, causing pain and discomfort in the affected area. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments is crucial for effective management and recovery.
Symptoms
The primary symptoms of bicep tendonitis include:
- Pain and tenderness: This is usually felt at the front of the shoulder and can extend down the arm.
- Weakness: Difficulty performing overhead activities or lifting objects.
- Swelling: Mild swelling around the shoulder or elbow.
- Clicking or snapping sound: This may occur when moving the shoulder.
- Night pain: Symptoms often worsen at night, disrupting sleep.
Causes
Bicep tendonitis can result from various factors, including:
- Repetitive overhead movements: Activities such as throwing, swimming, and weightlifting.
- Sudden injury: Acute injuries from falls or lifting heavy objects.
- Poor posture: Chronic poor posture can strain the shoulder tendons.
- Age-related degeneration: Tendons naturally weaken with age, making them more susceptible to inflammation.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing bicep tendonitis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests. Healthcare providers may use:
- Physical examination: Assessing range of motion, strength, and signs of instability.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI scans to confirm inflammation and rule out other conditions.
Effective Treatments
Treatment for bicep tendonitis ranges from conservative methods to surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition.
- Conservative Treatments
- Rest and activity modification: Avoid activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Cold packs: Applying ice to reduce swelling and pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Exercises to improve range of motion, strength, and stability of the shoulder and biceps.
- Steroid injections: Corticosteroid injections can provide significant pain relief and reduce inflammation.
Surgical Treatments
- Biceps tenodesis: Removing the damaged section of the tendon and reattaching the remaining portion to the humerus.
- Tenotomy: Releasing the damaged tendon from its attachment, often resulting in a “Popeye” bulge but effectively reducing pain.
Prevention
Preventing bicep tendonitis involves maintaining good shoulder health through:
- Regular exercise: Strengthening shoulder and upper back muscles.
- Proper technique: Using correct techniques during physical activities to avoid strain.
- Ergonomics: Ensuring proper posture and ergonomic setups at work and during sports.
FAQs
Q: Can bicep tendonitis heal on its own? A: Mild cases can improve with rest, ice, and NSAIDs. However, persistent symptoms may require physical therapy or medical intervention.
Q: How long does recovery take? A: Recovery time varies. Non-surgical treatment may take a few weeks, while surgical recovery can take several months, depending on the individual and the extent of the injury.
Q: Is surgery always necessary for bicep tendonitis? A: No, surgery is typically considered only when conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there is a complete tendon tear.
Q: Can I continue exercising with bicep tendonitis? A: It’s important to avoid activities that worsen the pain. Consult a healthcare provider or physical therapist for a tailored exercise program.
Conclusion
Bicep tendonitis, while painful and limiting, can be effectively managed with the right combination of treatments. Early diagnosis and appropriate interventions are key to a full recovery and prevention of further complications.