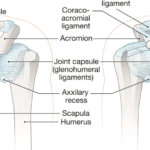
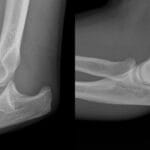
Sleep is a fundamental biological process that plays a crucial role in overall health and well-being. Beyond its restorative functions for the mind, sleep is integral to physical healing, particularly in the recovery from injuries. Arm injuries, encompassing conditions such as fractures, sprains, strains, and overuse injuries like tendinitis, require effective healing strategies to restore function and alleviate pain. Understanding the role of sleep in the healing process of arm injuries is essential for optimizing recovery outcomes.
The Physiology of Sleep and Its Impact on Healing
Sleep is categorized into two primary types: Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) sleep and Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. NREM sleep is further divided into three stages, with Stage 3, known as slow-wave sleep or deep sleep, being particularly significant for physical restoration.
During this stage, the body releases growth hormones that are vital for tissue repair and muscle growth.
This hormonal activity facilitates the healing of damaged tissues, including those in the arms, by promoting protein synthesis and the regeneration of muscle fibers.
Additionally, sleep enhances immune function by promoting the production of cytokines, proteins that play a role in combating infections and inflammation. Adequate sleep ensures a robust immune response, which is essential for preventing infections at injury sites and facilitating the overall healing process.
Sleep Duration and Quality in Injury Recovery
The duration and quality of sleep are critical factors influencing the recovery from arm injuries. Adults are generally recommended to obtain 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support optimal physiological functions. In the context of injury recovery, sufficient sleep duration allows for extended periods of tissue repair and regeneration. Conversely, sleep deprivation can impair these processes, leading to prolonged healing times and an increased risk of re-injury.
Sleep quality, characterized by uninterrupted and restful sleep, is equally important. Factors such as pain and discomfort from arm injuries can disrupt sleep patterns, resulting in fragmented sleep. Implementing pain management strategies and creating a conducive sleep environment can help improve sleep quality, thereby enhancing the healing process.
The Interrelationship Between Sleep and Pain Perception
Sleep and pain share a bidirectional relationship. Poor sleep can heighten pain sensitivity, while increased pain can lead to sleep disturbances. This cycle can be particularly detrimental in the context of arm injuries, where pain is a prominent symptom. Addressing sleep issues through interventions such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) or appropriate use of analgesics can break this cycle, reducing pain perception and promoting better sleep, which in turn facilitates healing.
Practical Strategies to Enhance Sleep for Arm Injury Recovery
To optimize sleep and support the healing of arm injuries, consider the following strategies:
Pain Management: Utilize prescribed pain relievers or non-pharmacological methods such as ice application and elevation to reduce pain before bedtime.
Sleep Positioning: Adopt sleep positions that minimize pressure on the injured arm. Using pillows to support the arm can alleviate discomfort and prevent inadvertent movements during sleep.
Sleep Environment: Create a comfortable sleep environment by ensuring a dark, quiet, and cool room. Investing in a supportive mattress and pillows can also enhance sleep quality.
Sleep Routine: Establish a consistent sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same times each day. Engaging in relaxing activities before bedtime, such as reading or gentle stretching, can signal the body to prepare for sleep.
Limit Stimulants: Avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime, as they can interfere with the ability to fall asleep.
Conclusion
Sleep is a vital component of the healing process for arm injuries. By understanding and prioritizing quality sleep, individuals can enhance tissue repair, modulate pain perception, and strengthen immune function, all of which contribute to a more efficient recovery. Integrating good sleep hygiene practices into recovery plans is essential for optimal healing outcomes.