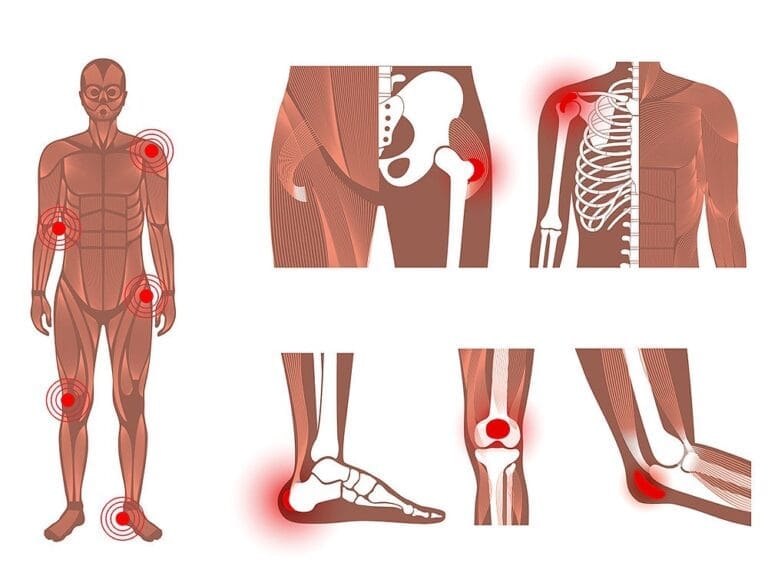
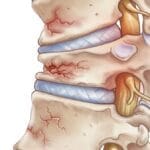
Orthopaedic surgery is a vital medical specialty that focuses on diagnosing, treating, and preventing disorders of the musculoskeletal system, including bones, muscles, joints, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and soft tissues. These surgical procedures are essential for restoring function and alleviating pain caused by various injuries and conditions.
Understanding Orthopaedic Surgery
Orthopaedic surgery involves surgical interventions to address issues related to the musculoskeletal system. These surgeries can correct deformities, repair injuries, and improve the function of affected body parts. Common orthopaedic surgeries include procedures like ACL reconstruction and knee replacements, often necessary due to sports injuries or degenerative joint diseases.
Types of Orthopaedic Surgery
Orthopaedic surgeons may specialise in specific areas of the body, such as:
- Hip and Knee: Procedures like hip replacements and knee arthroscopy.
- Hand and Wrist: Surgeries to correct carpal tunnel syndrome or repair fractures.
- Foot and Ankle: Treatments for conditions like bunions or Achilles tendon injuries.
- Spine: Surgeries to address spinal deformities or herniated discs.
- Shoulder and Elbow: Procedures for rotator cuff repairs or elbow reconstructions.
Subspecialties also include:
- Oncology: Treatment of bone tumors.
- Trauma: Emergency procedures for fractures and acute injuries.
- Sports Medicine: Focused on sports-related injuries.
- Pediatric Orthopaedics: Specialized care for children’s musculoskeletal issues.
Conditions Treated by Orthopaedic Surgery
Orthopaedic surgery addresses a wide range of conditions, including:
- Joint pain from arthritis.
- Muscle and ligament tears.
- Bone fractures.
- Congenital deformities.
- Tumours within the musculoskeletal system.
Preparing for Orthopaedic Surgery in the UK
Preparation for orthopaedic surgery typically starts with a consultation where the surgeon evaluates your condition, reviews your medical history, and conducts necessary imaging tests like X-rays or MRIs. This initial evaluation helps the surgeon plan the appropriate surgical intervention.
The Surgical Procedure
On the day of surgery, patients are admitted to a hospital or specialised clinic. The surgical team prepares the patient, administers anaesthesia, and performs the surgery. Procedures can include:
- Fixing broken bones with rods or screws.
- Replacing damaged joints with prosthetics.
- Repairing torn ligaments or tendons.
Recovery and Aftercare
Post-surgery, patients are monitored in a recovery room before being discharged or transferred to a ward for further observation. Recovery involves rest, physical therapy, and regular follow-up appointments to track healing progress. The UK healthcare system ensures comprehensive postoperative care, including detailed instructions for at-home care and physical rehabilitation to facilitate recovery.
When to Contact Your Doctor
Patients should contact their healthcare provider if they experience severe pain, signs of infection (such as redness or swelling), or unusual discharge from the surgical site. Immediate medical attention ensures any complications are addressed promptly.
Orthopaedic surgery is a vital component of the UK healthcare system, significantly enhancing patient mobility and quality of life by addressing musculoskeletal issues effectively. The NHS and private healthcare providers offer extensive support and resources for patients undergoing these surgeries, ensuring optimal outcomes and swift recovery.