Overview:
Scapular fractures are rare and usually result from high-energy trauma. While most can be managed without surgery, certain fractures require surgical fixation to ensure proper healing and function.
What are Scapula and Glenoid Fossa Fractures?
- Scapula: The shoulder blade, a flat bone connecting the upper arm to the collarbone.
- Glenoid Fossa: The part of the scapula that forms the socket for the shoulder joint.
Causes of Scapula and Glenoid Fossa Fractures:
- High-Energy Trauma: Car accidents, motorcycle crashes, or falls from height.
- Direct Impact: A heavy blow to the shoulder.
Symptoms:
- Pain: Severe pain in the shoulder.
- Swelling and Bruising: Visible swelling and bruising around the shoulder.
- Limited Movement: Difficulty moving the arm.
Diagnosing Scapula and Glenoid Fossa Fractures:
- Physical Examination: Checking for pain, swelling, and deformity.
- Imaging:
- X-rays: Standard views to see the fracture.
- CT Scans: For detailed images, especially for surgical planning.
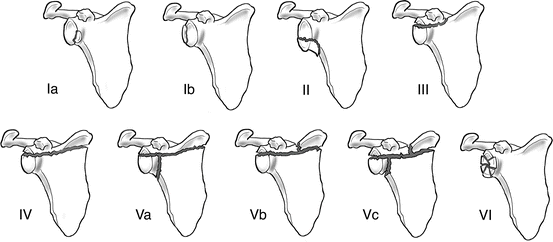
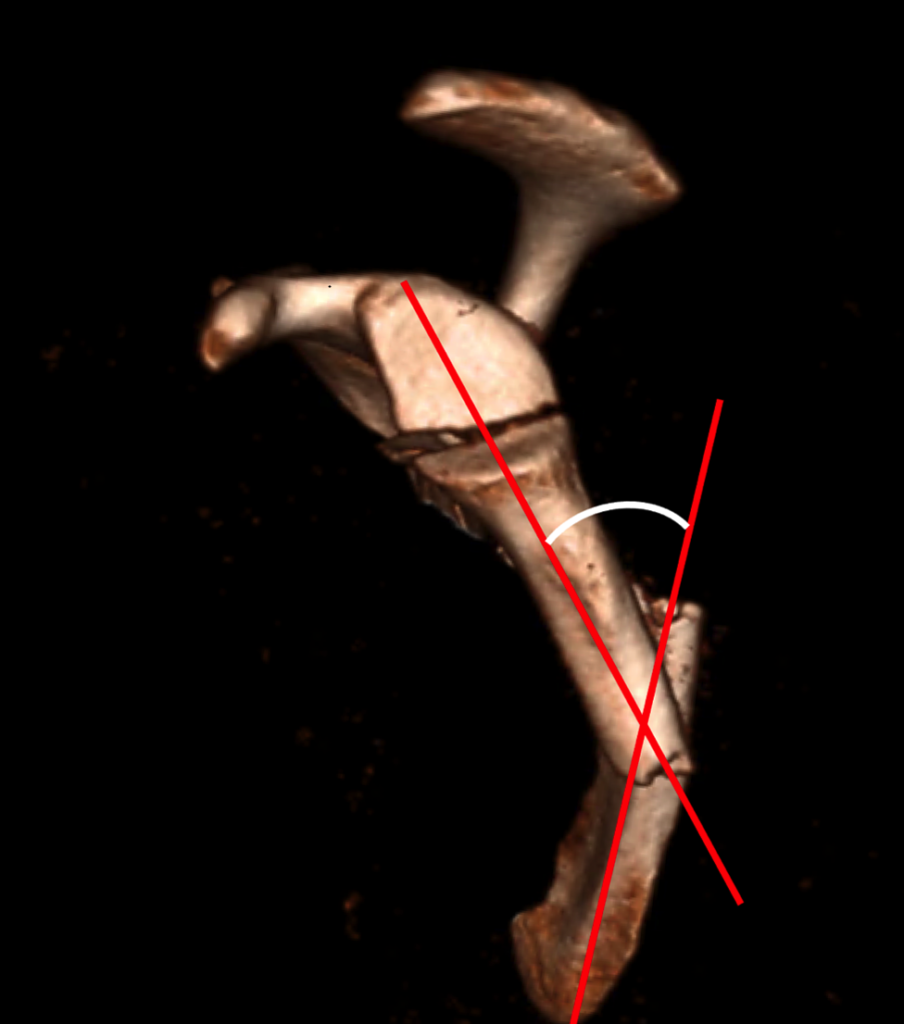
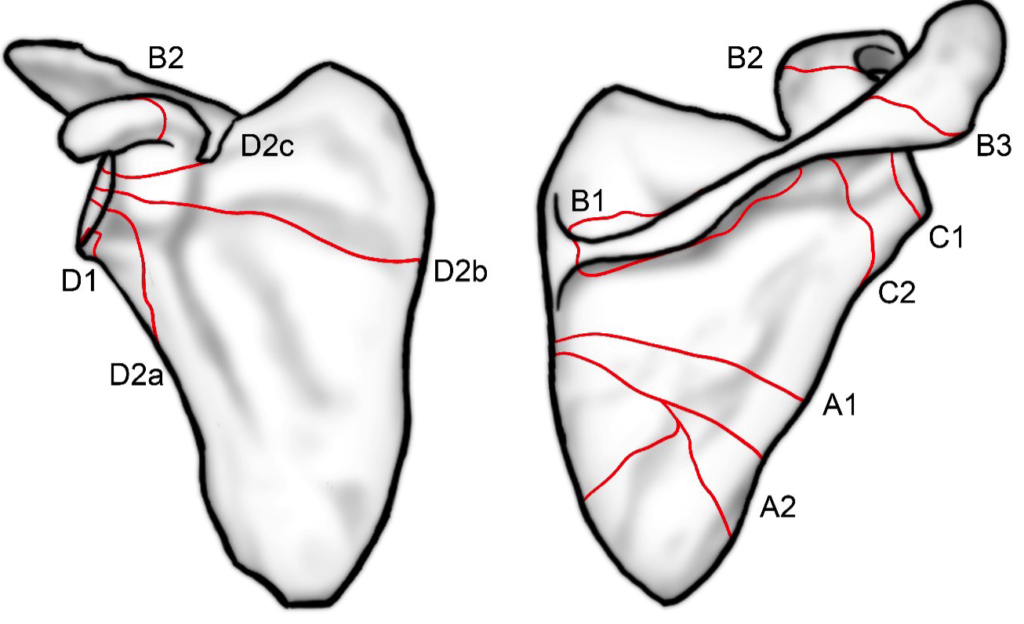
Types of Fractures:
- Euler and Habermeyer Classification: Categorizes fractures based on their location and severity.
- Ideberg Classification: Focuses on glenoid fractures with various extensions.
Treatment Options:
- Non-Surgical Management:
- Suitable for most minimally displaced fractures.
- Supportive Sling: To immobilize the arm.
- Gradual Exercises: To restore movement and strength over 4-6 weeks.
- Surgical Management:
- Needed for significantly displaced or unstable fractures.
- Surgical Techniques: Various approaches to realign and fix the bones using plates and screws.
Possible Complications:
- Infection: Risk after surgery.
- Implant Issues: Problems with surgical hardware.
- Non-Union: Bone fails to heal.
- Malunion: Bone heals incorrectly.
Lessons Learned:
- Thorough assessment and imaging are crucial.
- Non-surgical treatment works for most minimally displaced fractures.
- Surgery is necessary for significantly displaced or unstable fractures.
- Post-operative rehabilitation and regular follow-up are essential for optimal outcomes.