Overview:
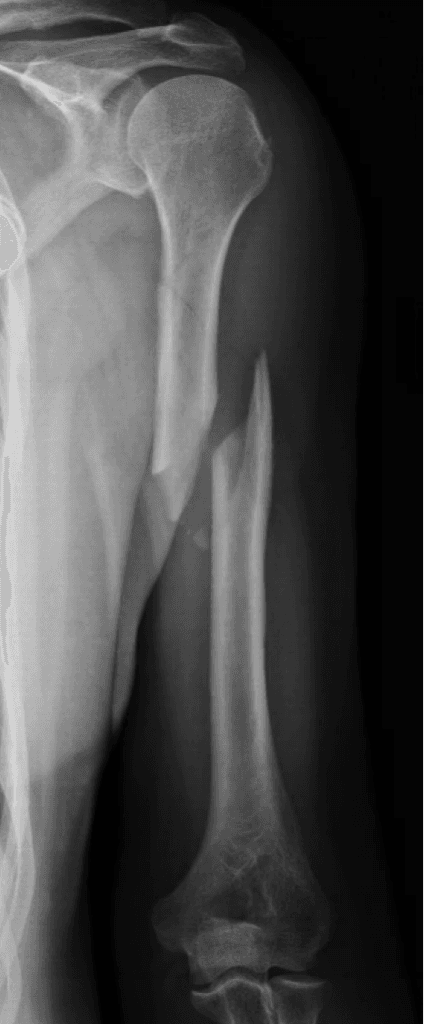
Diaphyseal humeral fractures are breaks in the middle section of the arm bone. These fractures occur from both high-energy trauma in younger people and low-energy falls in older adults.
What is the Diaphyseal Humerus?
The diaphyseal humerus is the long, middle part of the arm bone.
Causes of Diaphyseal Humeral Fractures:
- Direct Trauma: Such as a direct blow to the arm.
- Indirect Mechanisms: Falls onto an outstretched arm or twisting injuries.
Symptoms:
- Pain: Severe pain at the site of the fracture.
- Swelling and Deformity: Visible swelling and possible deformity.
- Limited Movement: Difficulty moving the arm.
Diagnosing Diaphyseal Humeral Fractures:
- Physical Examination: Checking for pain, swelling, and deformity.
- Imaging:
- X-rays: Standard views to see the fracture.
- CT Scans: For detailed images if needed.
Types of Fractures:
- AO-OTA Classification: Divides fractures into simple (A), wedge (B), and complex (C) types.
Treatment Options:
- Non-Surgical Management:
- Suitable for many diaphyseal humeral fractures.
- Functional Bracing: A special brace to support the arm and allow healing.
- Early Mobilization: Gradual movement exercises to prevent stiffness.
- Surgical Management:
- Needed for fractures with significant displacement or complications.
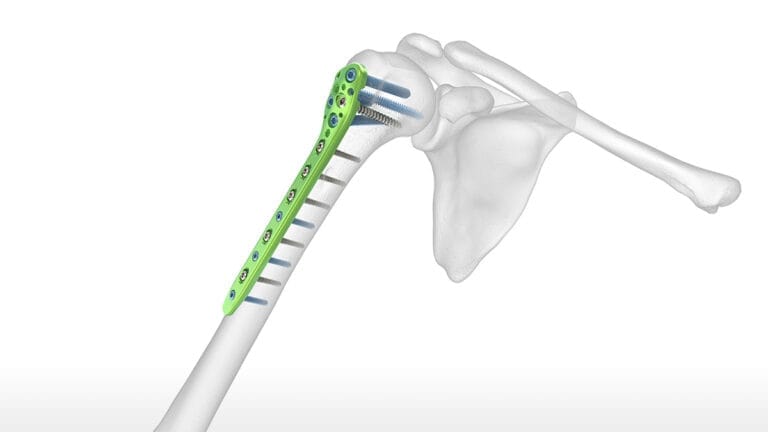
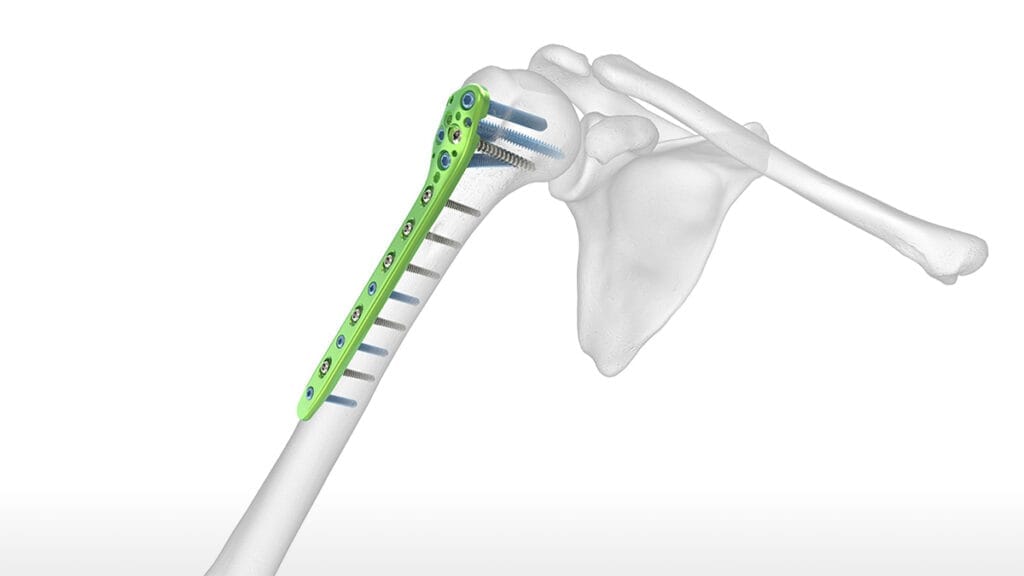
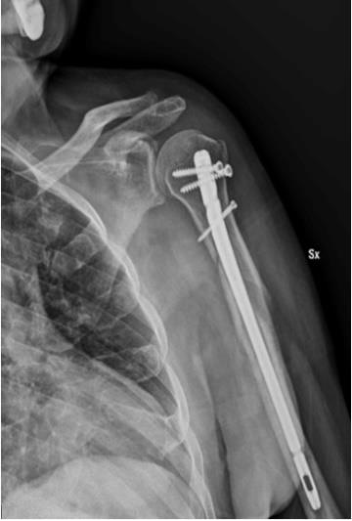
- ORIF (Open Reduction and Internal Fixation): Aligning and fixing the bones with plates and screws.
- Intramedullary Nailing (IMN): Inserting a rod into the bone to stabilize the fracture.
Possible Complications:
- Radial Nerve Palsy: Injury to the nerve, affecting arm movement.
- Infection: Risk after surgery.
- Non-Union: Bone fails to heal.
- Malunion: Bone heals incorrectly.
Lessons Learned:
- Accurate diagnosis and imaging are essential.
- Non-surgical treatment with functional bracing works for many fractures.
- Surgery is necessary for more complex fractures.
- Early mobilization and follow-up are crucial for healing.
- Individualized treatment plans based on the fracture and patient factors lead to the best outcomes.