Introduction
Arm pain is a common condition affecting people of all ages. Whether caused by injuries, repetitive strain, arthritis, or nerve-related conditions, managing arm pain effectively is essential for maintaining daily function. One of the non-invasive, drug-free treatments gaining popularity is Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) therapy.
This article explores how to use TENS therapy for arm pain relief, including its mechanism, benefits, correct usage, electrode placement, safety considerations, and scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness. This guide is fully optimized for SEO best practices, ensuring maximum visibility on search engines.
1. Understanding TENS Therapy
1.1 What Is TENS Therapy?
TENS therapy is a form of electrotherapy that uses low-voltage electrical currents to stimulate nerves and reduce pain. It is applied through electrode pads placed on the skin near the painful area.
1.2 How Does TENS Therapy Work?
TENS therapy works through two main mechanisms:
- Gate Control Theory: Electrical impulses block pain signals from reaching the brain.
- Endorphin Release: Stimulates the body to release natural painkillers (endorphins).
1.3 Benefits of TENS Therapy
- Non-invasive and drug-free pain relief.
- Reduces inflammation and muscle spasms.
- Can be used alongside other treatments (physiotherapy, medications).
- Portable and easy to use at home.
2. Causes of Arm Pain and How TENS Can Help
TENS therapy is effective for various conditions causing arm pain:
2.1 Musculoskeletal Causes
- Tendinitis (inflammation of tendons, e.g., rotator cuff tendinitis).
- Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis).
- Golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis).
- Osteoarthritis in the elbow or shoulder.
2.2 Nerve-Related Causes
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (nerve compression in the wrist).
- Cervical radiculopathy (pinched nerve in the neck causing arm pain).
- Peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage leading to tingling and pain).
2.3 Post-Surgical or Injury-Related Pain
- Post-fracture pain during recovery.
- Soft tissue injuries (sprains, strains).
3. How to Use a TENS Unit for Arm Pain Relief
3.1 Choosing the Right TENS Unit
TENS units vary in features, including:
- Adjustable intensity levels.
- Multiple electrode channels for larger treatment areas.
- Pre-programmed settings for different pain types.
3.2 Understanding TENS Settings
- Pulse Frequency (Hz): Low (2–10 Hz) for chronic pain, high (50–100 Hz) for acute pain.
- Pulse Duration (μs): Short for nerve pain, longer for deep tissue pain.
- Intensity Level: Should be strong but comfortable, not painful.
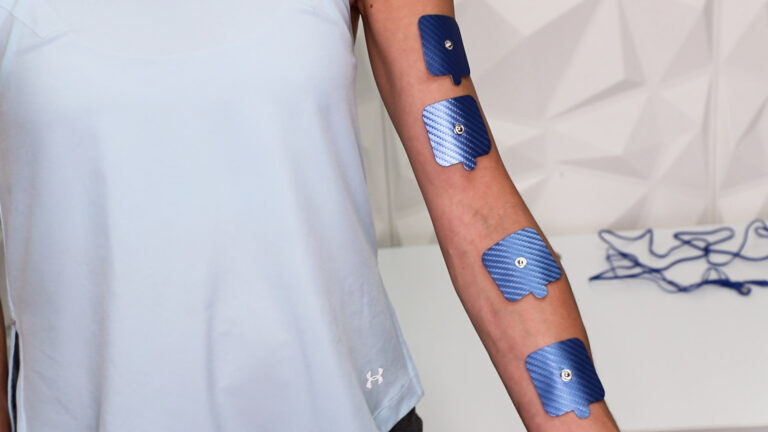
3.3 Best Electrode Placement for Arm Pain
For Shoulder Pain
- Place two electrodes on the upper shoulder area.
- Another two electrodes can be placed around the deltoid muscle.
For Elbow Pain (Tennis or Golfer’s Elbow)
- One electrode near the pain point on the elbow.
- Another electrode on the forearm muscle.
For Wrist and Hand Pain (Carpal Tunnel)
- Electrodes placed near the wrist and forearm.
- Avoid placing directly on the carpal tunnel nerve.
For Nerve-Related Arm Pain
- Place electrodes along the nerve pathway.
- Use symmetrical placement for even stimulation.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Using TENS for Arm Pain
- Clean the skin where electrodes will be placed.
- Attach the electrodes in the correct locations.
- Turn on the TENS unit and adjust settings.
- Start at a low intensity and gradually increase.
- Use for 15–30 minutes per session, up to 3 times per day.
- Turn off the device before removing electrodes.
5. Safety Considerations and Precautions
5.1 Who Should Not Use TENS?
- Pregnant women (avoid abdomen area).
- People with pacemakers (electrical interference risk).
- Individuals with epilepsy (risk of triggering seizures).
5.2 Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Placing electrodes over broken skin.
- Using TENS too frequently (limit sessions to prevent overstimulation).
- Setting the intensity too high, which can cause discomfort.
6. Scientific Evidence Supporting TENS for Arm Pain
6.1 Studies on Musculoskeletal Pain
- Research has shown that TENS therapy significantly reduces pain in conditions like tennis elbow and osteoarthritis.
- A 2020 study found that TENS improves grip strength and reduces elbow pain in lateral epicondylitis patients.
6.2 Studies on Nerve Pain
- A clinical trial in 2018 demonstrated that TENS reduces pain intensity and improves nerve function in carpal tunnel syndrome.
6.3 TENS vs. Other Pain Relief Methods
- Compared to medication, TENS has fewer side effects.
- Physiotherapy combined with TENS is more effective than either treatment alone.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
7.1 Can TENS Cure Arm Pain Permanently?
TENS provides temporary pain relief but does not cure the underlying condition. Consistent use along with physical therapy may improve long-term outcomes.
7.2 How Long Should I Use TENS Per Session?
Use TENS for 15–30 minutes per session, 2–3 times per day.
7.3 Can I Sleep with a TENS Unit On?
No, it is not recommended to use TENS while sleeping due to overstimulation risks.
7.4 Does TENS Work Immediately?
Many users experience immediate relief, but the effect may last for a few hours.
7.5 How Do I Know If TENS Is Working?
You should feel a comfortable tingling sensation without pain.
8. Conclusion
TENS therapy is a safe, effective, and drug-free method for relieving arm pain caused by musculoskeletal injuries, nerve compression, and post-surgical recovery. With correct electrode placement, proper settings, and regular use, TENS can significantly improve pain management and mobility.