Introduction
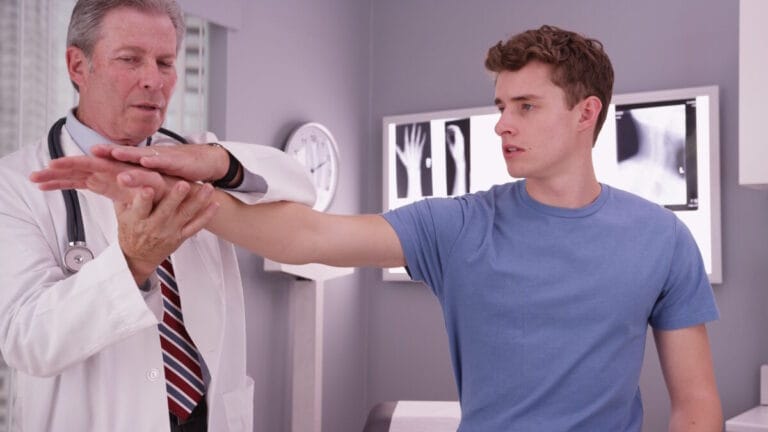
Choosing the right orthopaedic specialist for your arm injury is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your recovery and overall health. Whether you’re dealing with a fracture, tendonitis, or a repetitive strain injury, finding a qualified and experienced orthopaedic specialist is essential to receiving the best care possible. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of selecting the right orthopaedic specialist, covering key factors to consider, the importance of board certification, and frequently asked questions to ensure you make an informed decision.
Chapter 1: Understanding Orthopaedic Specialization
What Is an Orthopaedic Specialist?
Orthopaedic specialists are medical doctors who focus on diagnosing, treating, and preventing disorders and injuries related to the musculoskeletal system, which includes bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. They are trained to manage conditions ranging from acute injuries to chronic musculoskeletal diseases.
Types of Orthopaedic Specialists
- General Orthopaedic Surgeons: These specialists treat a wide variety of musculoskeletal conditions and are often the first point of contact for patients with bone or joint issues.
- Hand and Wrist Specialists: Focus on conditions affecting the hands, wrists, and forearms, making them particularly relevant for arm injuries.
- Sports Medicine Orthopaedists: These specialists often treat injuries related to sports and physical activities, including repetitive strain injuries in the arm.
- Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgeons: Specialize in treating musculoskeletal issues in children, which can differ significantly from those in adults.
- Trauma Surgeons: Focus on acute injuries, such as fractures and dislocations, often resulting from accidents or falls.
Why Choose an Orthopaedic Specialist for Arm Injuries?
Arm injuries, such as fractures, tendon tears, and repetitive strain injuries, often require specialized care. An orthopaedic specialist with experience in treating arm injuries can provide the most accurate diagnosis, effective treatment plans, and appropriate surgical interventions if necessary. Their expertise ensures that you receive tailored care that addresses the unique aspects of arm injuries.
Chapter 2: Qualifications and Credentials
Educational Background and Training
Orthopaedic specialists undergo extensive education and training, including:
- Medical School: Completion of a medical degree (MD or DO) is the first step, where the doctor gains a broad understanding of human anatomy, physiology, and pathology.
- Residency: Following medical school, orthopaedic surgeons complete a five-year residency program focusing on orthopaedic surgery, where they gain hands-on experience in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal conditions.
- Fellowship: Many orthopaedic specialists pursue additional fellowship training in a specific area, such as hand surgery, sports medicine, or trauma. This additional training allows them to develop expertise in treating specific types of injuries and conditions.
Board Certification
Board certification is a critical factor when choosing an orthopaedic specialist. In the United States, the American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery (ABOS) certifies orthopaedic surgeons who meet rigorous standards of education, experience, and ethical practice. Certification indicates that the specialist has demonstrated the necessary knowledge and skills to provide high-quality care.
Licensing and State Regulations
Orthopaedic specialists must be licensed to practice in their respective states. Licensing requirements vary by state but generally include passing a comprehensive exam and completing continuing education to stay current with medical advancements.
Experience and Specialization
Experience is particularly important when choosing an orthopaedic specialist for an arm injury. Consider the following:
- Years in Practice: How long has the specialist been practicing orthopaedic surgery?
- Number of Procedures: How many procedures related to your specific injury has the specialist performed?
- Success Rates: What are the specialist’s outcomes for similar cases?
Chapter 3: How to Find the Right Orthopaedic Specialist
Step 1: Get Referrals
Start by asking your primary care physician for a referral to a qualified orthopaedic specialist. You can also seek recommendations from:
- Friends and Family: People you trust who have had similar injuries may provide valuable insights.
- Other Healthcare Providers: Physical therapists, chiropractors, or other specialists who regularly work with orthopaedic surgeons may have good recommendations.
Step 2: Research Potential Specialists
Once you have a list of potential specialists, research each one:
- Check Credentials: Verify their board certification, licensing, and any fellowship training.
- Read Patient Reviews: Look for patient testimonials on healthcare websites. Pay attention to reviews that discuss the specialist’s communication style, bedside manner, and outcomes.
- Consider Hospital Affiliations: The quality of the hospital where the specialist practices can impact your care. Look for specialists affiliated with top-rated hospitals.
Step 3: Evaluate Communication Style
Effective communication is crucial for a successful patient-doctor relationship. During your initial consultation, consider:
- Listening Skills: Does the specialist listen carefully to your concerns and questions?
- Clarity: Does the specialist explain your diagnosis and treatment options in a way that is easy to understand?
- Comfort Level: Do you feel comfortable discussing your condition with the specialist? Do they respect your opinions and concerns?
Step 4: Consider Practical Factors
Practical considerations are also important when choosing an orthopaedic specialist:
- Location: Choose a specialist whose office is conveniently located, especially if you require frequent visits.
- Availability: Consider the specialist’s office hours and whether they offer flexible scheduling.
- Insurance: Ensure the specialist accepts your insurance plan to avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
Chapter 4: Treatment Options for Arm Injuries
Non-Surgical Treatments
Before recommending surgery, most orthopaedic specialists will explore non-surgical treatment options. These may include:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises and stretches to improve mobility, strength, and flexibility in the affected arm.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Bracing or Splinting: Immobilizing the affected area to prevent further injury and promote healing.
- Activity Modification: Adjusting your daily activities to avoid putting stress on the injured arm.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation in cases of tendonitis or bursitis.
Surgical Treatments
If non-surgical treatments are ineffective, surgery may be necessary. Common surgical procedures for arm injuries include:
- Fracture Repair: Using plates, screws, or rods to stabilize and heal broken bones.
- Tendon Repair: Reattaching or reconstructing torn tendons in the arm or shoulder.
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure that allows the surgeon to diagnose and treat joint problems using a small camera and specialized instruments.
- Joint Replacement: In severe cases, such as advanced arthritis, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to restore function.
Post-Surgical Care and Rehabilitation
Recovery from arm surgery requires a well-structured rehabilitation plan, which may include:
- Physical Therapy: To restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Pain Management: Using medications or other therapies to manage post-operative pain.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular visits to monitor healing and address any complications.
Chapter 5: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do I know if I need to see an orthopaedic specialist for my arm injury?
You should see an orthopaedic specialist if you experience persistent pain, swelling, limited range of motion, or suspect a fracture or tendon injury. If your arm injury is not improving with rest and over-the-counter treatments, it’s time to seek specialized care.
What should I expect during my first visit to an orthopaedic specialist?
During your first visit, the orthopaedic specialist will review your medical history, ask about your symptoms, and perform a physical examination. They may also order imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRIs, to get a better understanding of your injury. Based on their findings, they will discuss treatment options with you, which may include physical therapy, medications, or surgery.
How important is it to choose a board-certified orthopaedic specialist?
Choosing a board-certified orthopaedic specialist is crucial because it ensures the doctor has met the rigorous standards set by the certifying board. It also indicates that they have the necessary knowledge and skills to provide high-quality care. Board certification is an additional level of trust that the specialist is well-qualified to treat your condition.
Can I get a second opinion if I’m unsure about my treatment plan?
Yes, getting a second opinion is a good idea if you are unsure about your diagnosis or treatment plan. A second opinion can provide additional perspectives and help you make a more informed decision about your care. Many patients seek second opinions, especially when surgery is recommended, to ensure they are making the best choice for their health.
What questions should I ask my orthopaedic specialist before surgery?
Before surgery, ask your orthopaedic specialist the following questions:
- What is the specific procedure you recommend, and why?
- What are the risks and benefits of this surgery?
- How long will the recovery process take?
- What are the potential complications?
- How many times have you performed this procedure, and what are your success rates?
- Are there non-surgical alternatives that I should consider?
How can I prepare for surgery on my arm?
To prepare for arm surgery, follow these steps:
- Follow any pre-operative instructions from your specialist, such as fasting or adjusting medications.
- Arrange for someone to drive you to and from the hospital or surgery center.
- Prepare your home for recovery by setting up a comfortable resting area and organizing essential items within easy reach.
- Discuss any concerns with your specialist, including pain management and post-operative care.
What are the common complications after arm surgery?
Common complications after arm surgery include:
- Infection: Proper wound care and hygiene can reduce the risk of infection.
- Blood Clots: Early mobilization and sometimes medications can prevent blood clots.
- Nerve Damage: Although rare, nerve damage can occur during surgery, leading to numbness, weakness, or pain.
- Stiffness and Scar Tissue: Physical therapy can help prevent stiffness and excessive scar tissue formation.
How long does it take to recover from arm surgery?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s overall health. Minor procedures may require only a few weeks of recovery, while more extensive surgeries, such as joint replacement or tendon repair, may take several months to a year. Following your specialist’s post-operative care instructions is crucial for a successful recovery.
Can physical therapy help prevent the need for surgery?
Yes, physical therapy can sometimes prevent the need for surgery, especially in cases of mild to moderate injuries. A physical therapist can design a rehabilitation program to strengthen the muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain, potentially avoiding the need for surgical intervention.
What should I do if I’m not satisfied with my orthopaedic specialist’s care?
If you’re not satisfied with your orthopaedic specialist’s care, consider the following steps:
- Discuss Your Concerns: Talk openly with your specialist about your concerns. They may address your issues or adjust your treatment plan.
- Seek a Second Opinion: If you’re still unsatisfied, seeking a second opinion from another orthopaedic specialist can provide clarity and reassurance.
- Change Specialists: If necessary, you have the right to change specialists. Look for a new orthopaedic specialist who better meets your needs and communication preferences.
Conclusion
Choosing the right orthopaedic specialist for your arm injury is a critical step in ensuring a successful recovery and maintaining long-term arm health. By considering factors such as board certification, experience, communication style, and practical logistics, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs. Remember to ask questions, seek referrals, and trust your instincts when selecting a specialist. With the right care, you can effectively manage your arm injury and regain full function.