Introduction
Low back pain is a common condition that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. It can range from a mild, occasional nuisance to a debilitating condition that severely impacts daily life. Understanding the various treatment options available is crucial for managing and alleviating this type of pain effectively.
Understanding Low Back Pain
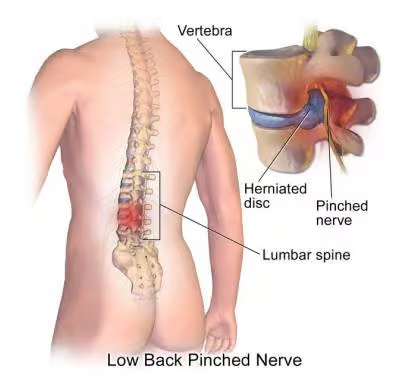
Low back pain can arise from a variety of causes, including muscle strain, ligament sprain, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and other degenerative conditions. Proper diagnosis by a healthcare professional is essential to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment plan.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
For many individuals, low back pain can be effectively managed with non-surgical treatments. These options include:
- Medications
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen and aspirin can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Prescription Medications: For more severe pain, doctors may prescribe stronger painkillers, muscle relaxants, or anti-inflammatory medications.
- Physiotherapy
- Exercise Regimens: Tailored exercises to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improve flexibility, and promote proper posture can be highly beneficial.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques such as massage, manipulation, and mobilisation performed by a trained therapist can provide relief.
- Lifestyle Modifications
- Activity Modification: Adjusting daily activities to avoid movements that exacerbate pain.
- Ergonomics: Improving workplace ergonomics, such as chair support and desk height, can prevent strain on the lower back.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on the lower back.
- Complementary Therapies
- Acupuncture: Some patients find relief through acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine technique.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal adjustments performed by a chiropractor can help alleviate pain in some cases.
- Yoga and Pilates: These practices can improve strength, flexibility, and overall spinal health.
Minimally Invasive Procedures When conservative treatments do not provide sufficient relief, minimally invasive procedures may be considered:
- Epidural Steroid Injections
- Steroid injections into the epidural space can reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
- Nerve Blocks
- Injections of anaesthetic near specific nerves can help block pain signals from reaching the brain.
- Radiofrequency Ablation
- This technique uses heat to disrupt nerve function and reduce pain.
Surgical Treatment Options Surgery is typically considered a last resort when other treatments have failed, and the pain significantly impacts quality of life. Surgical options include:
- Discectomy
- Removal of the herniated portion of a disc to relieve pressure on a nerve.
- Laminectomy
- Removal of part of the vertebra to create more space for the spinal nerves.
- Spinal Fusion
- Fusing two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine.
- Artificial Disc Replacement
- Replacing a damaged disc with an artificial one to maintain spine movement.
Conclusion
Effective management of low back pain often requires a combination of treatments tailored to the individual’s specific condition and needs. From non-surgical options like medications and physical therapy to minimally invasive procedures and surgery, a wide range of treatments is available. Consulting with healthcare professionals to develop a personalised treatment plan is essential for achieving the best outcomes and improving quality of life.