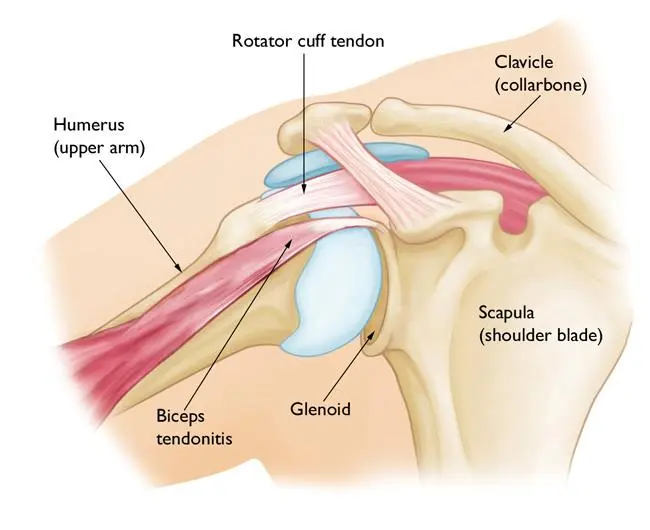
The biceps muscle, located at the front of the upper arm, has two tendons that connect it to the bones of the shoulder and one tendon that attaches it to the radius bone at the elbow. These tendons are crucial for movement, but they can suffer from injuries such as tendonitis and tears.
Types of Biceps Tendon Injuries
- Proximal Biceps Tendonitis at Shoulder
- Proximal Biceps Tendon Tear at Shoulder
- Distal Biceps Tendonitis and Tear at Elbow
When the biceps tendon at the shoulder is torn, it can lead to a loss of arm strength and pain when rotating the arm. Many individuals can still manage with simple treatments, but surgery might be necessary if nonsurgical methods fail to restore strength and alleviate symptoms.
Anatomy
The biceps tendon has two attachment points at the shoulder joint. The upper arm bone fits into the glenoid socket of the shoulder blade, stabilized by the rotator cuff, a combination of muscles and tendons.
Biceps Tendonitis
What is Biceps Tendonitis? Biceps tendonitis occurs when the tendon becomes sore and painful due to overuse or a sudden heavy load. This condition is common in athletes and individuals engaged in repetitive motion activities.
How is Biceps Tendonitis Treated?
- Non-operative Treatment
- Use cold packs or ice to reduce swelling and pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications like naproxen or ibuprofen.
- Rest, avoiding heavy lifting and elbow flexing.
- Physical therapy might be recommended.
- In severe cases, corticosteroid injections, platelet-rich plasma, or stem cells may be used.
Preventative measures include avoiding activities that cause overuse and correcting any underlying conditions like improper posture or poor technique.
Biceps Tendon Tears
What are Biceps Tendon Tears? Tendon tears can occur from overuse or injury. They can be partial or complete, with complete tears splitting the tendon into two pieces. The long head of the biceps tendon is more prone to injury due to its location.
Causes of Long Head of Biceps Tears
- Injury: Sudden falls or lifting heavy objects can cause tears.
- Overuse: Repetitive motions over time can wear down the tendon.
Risk Factors
- Age
- Heavy overhead activities
- Repetitive sports
- Smoking
- Corticosteroid medications
Symptoms of Biceps Tendon Tear
- Sudden, severe pain in the upper arm or elbow.
- A “pop” sound at the time of the tear.
- Cramping, bruising, pain, tenderness, and weakness in the shoulder or elbow.
- A bulge in the upper arm above the elbow.
Imaging Tests
- X-rays: Rule out other issues causing pain.
- MRI: Shows partial and complete tears in soft tissues.
Treatment of Shoulder Biceps Tears
Non-surgical Treatment
- Ice to reduce swelling.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications.
- Rest and avoidance of heavy lifting.
- Physiotherapy for flexibility and strength.
Surgical Treatment Surgery is considered when nonsurgical treatments fail to relieve symptoms or for complete strength recovery. The procedure involves reattaching the tendon to the bone, followed by rehabilitation with flexibility and strengthening exercises.
Conclusion
Biceps tendon injuries at the shoulder can significantly impact arm function. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, whether nonsurgical or surgical, can help restore strength and relieve pain. For more information on shoulder-related conditions and treatments,