Introduction
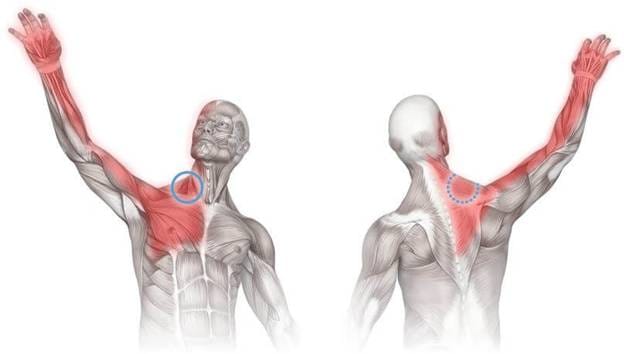
Arm pain resulting from repetitive motion is a common condition that affects a variety of people, from office workers to athletes. This type of pain, often referred to as a repetitive strain injury (RSI), occurs due to the continuous use of specific muscle groups in the arms, leading to inflammation, nerve damage, or muscle strain. Common examples include carpal tunnel syndrome, tennis elbow, and shoulder bursitis. Managing arm pain from repetitive motion requires a combination of preventative strategies, therapeutic interventions, and lifestyle adjustments.
What Causes Repetitive Motion Arm Pain?
Repetitive motion arm pain develops when the muscles, tendons, or nerves in the arm are overworked due to repetitive activities. Activities like typing, lifting, or performing repetitive athletic motions (such as swinging a tennis racket) can lead to microtrauma in these tissues over time. Factors that exacerbate the condition include poor posture, inadequate rest, and lack of proper warm-up before engaging in repetitive activities.
Common causes include:
- Typing or using a mouse for prolonged periods
- Heavy lifting or carrying
- Sports like tennis, golf, or baseball that require repetitive arm movements
- Manual labor, such as construction work or assembly line tasks
Common Symptoms of Repetitive Motion Injuries
Symptoms can vary depending on the severity and the location of the injury, but the most common signs of repetitive motion arm pain include:
- Persistent or intermittent pain in the arm, wrist, or shoulder
- Swelling or inflammation around the joints or tendons
- Stiffness and limited range of motion
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or fingers
- Weakness or difficulty gripping objects
Effective Management Techniques
Rest and Activity Modification
Rest is one of the most important factors in allowing injured muscles and tendons to heal. Avoid or modify the activities that are causing pain. For example, reduce time spent on tasks that require repetitive motions, or use ergonomic tools that minimize strain.
Ice and Heat Therapy
Using cold packs can help reduce inflammation, while heat therapy can soothe sore muscles. Apply ice for 15-20 minutes at a time during acute flare-ups, and consider using heat pads for chronic muscle soreness.
Stretching and Strengthening Exercises
Stretching and strengthening exercises can alleviate tension in the arm muscles. Some beneficial exercises include:
- Wrist flexor stretches: Extend your arm with the palm facing up, gently pull back on your fingers with the opposite hand.
- Forearm pronation/supination stretches: Use a small weight and rotate the forearm to relieve strain.
- Shoulder and neck stretches: These can help reduce tension that may radiate down the arms.
Incorporating strength training for the shoulder, wrist, and forearm muscles can help prevent future injury by improving muscle endurance.
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can design a program tailored to your injury, focusing on proper posture, ergonomic adjustments, and specific exercises. They may also use techniques such as massage, ultrasound therapy, or electrical stimulation to promote healing.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Ensure your workspace is ergonomically friendly. Adjusting your desk, chair, and computer setup can make a huge difference in preventing arm pain. Proper posture is essential, with your arms at a 90-degree angle, wrists neutral, and the monitor at eye level.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can reduce inflammation and manage pain. However, these should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare provider if taken long-term.
Use of Splints or Braces
Wrist splints or elbow braces can immobilize the affected area, allowing the muscles and tendons to rest. This is particularly useful for conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or tennis elbow.
Massage Therapy
Therapeutic massage can help loosen tight muscles and improve blood flow to the injured area. Regular massage therapy, in combination with other treatment methods, can reduce muscle tension and pain.
Steroid Injections
For severe cases, steroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation around tendons and joints. This is often considered after other conservative treatments have failed.
Surgery
In rare and severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgery might be necessary. This is common in cases of severe carpal tunnel syndrome or when there is tendon damage that cannot heal on its own.
Preventative Strategies for Repetitive Motion Injuries
Take Frequent Breaks
Incorporate frequent short breaks into your routine, especially during activities that require repetitive motions. Stretch your arms, wrists, and shoulders regularly to prevent stiffness.
Maintain Good Posture
Good posture is key to preventing strain. Ensure your shoulders are relaxed and not hunched, and avoid extending your wrists or elbows into awkward positions.
Warm-Up Before Activities
Before engaging in repetitive activities, especially sports, do a proper warm-up. Gentle stretching and dynamic movements can help prepare your muscles and joints for action.
Use Proper Technique
Whether typing, lifting, or playing sports, always use proper technique to reduce strain on the arms. Incorrect movement patterns can lead to overuse injuries.
Strengthen Supporting Muscles
Strengthen the muscles around the joints to provide better support and prevent strain. Focus on forearm, shoulder, and upper back exercises to create a strong foundation for arm movements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for repetitive motion arm pain to heal?
Healing time depends on the severity of the injury and the steps taken to rest and rehabilitate the affected area. Mild cases may heal within a few weeks with proper care, while more severe injuries can take several months.
Can repetitive motion injuries become permanent?
If left untreated, repetitive motion injuries can lead to chronic pain and permanent damage to the muscles, tendons, or nerves. Early intervention is crucial for preventing long-term issues.
What is the difference between a repetitive motion injury and arthritis?
Repetitive motion injuries are caused by overuse, while arthritis is an inflammatory condition that affects the joints. However, repetitive strain injuries can lead to conditions like bursitis or tendonitis, which may mimic the symptoms of arthritis.
Can I continue exercising if I have arm pain?
You can continue exercising, but it’s important to avoid activities that exacerbate the pain. Focus on low-impact exercises and stretches that don’t strain the affected muscles.
Are ergonomic tools effective in preventing repetitive motion injuries?
Yes, ergonomic tools such as split keyboards, adjustable chairs, and wrist rests can significantly reduce the strain placed on the muscles and tendons during repetitive tasks.
Conclusion
Managing arm pain from repetitive motion requires a combination of preventative measures, therapeutic interventions, and lifestyle modifications. By addressing the root cause of the pain and adopting strategies to relieve strain, it is possible to prevent further injury and promote healing. If you experience persistent pain, consulting a healthcare provider is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment