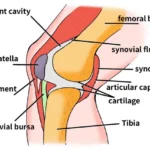
Arm injuries are common and can result from various activities, ranging from sports to daily chores. Understanding these injuries, their symptoms, and treatments is crucial for effective management and prevention. This guide covers the most common arm injuries, their treatments, and preventive measures, and includes an FAQ section to address common concerns.
Common Arm Injuries
Sprains and Strains
Sprains involve stretching or tearing ligaments, while strains involve muscles or tendons. These injuries often result from falls, twists, or direct impacts.
Symptoms:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Limited mobility
Treatment:
- Rest
- Ice application
- Compression with a bandage
- Elevation of the affected arm
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen
Biceps Tendinitis
This condition involves inflammation of the tendons connecting the biceps muscle to the shoulder and elbow. It is often caused by repetitive motions or overuse.
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness in the front of the shoulder or elbow
- Swelling
- Reduced range of motion
Treatment:
- Rest
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery
Bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa, a small fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between tissues. It commonly affects the elbow.
Symptoms:
- Pain
- Swelling
- Limited movement
Treatment:
- Rest
- Ice application
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Aspiration of excess fluid by a healthcare provider
Fractures
Fractures are breaks in the bone, often caused by trauma such as falls or direct blows.
Symptoms:
- Severe pain
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Deformity
- Inability to move the affected arm
Treatment:
- Immobilization with a cast or splint
- Pain management
- Surgery in severe cases
- Physical therapy post-healing
Dislocations
A dislocation occurs when the bones in a joint are forced out of their normal positions. The shoulder is a common site for dislocations.
Symptoms:
- Severe pain
- Swelling
- Visible deformity
- Inability to move the joint
Treatment:
- Immediate medical attention to reposition the bones
- Immobilization
- Pain relief
- Physical therapy to restore function
Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
This condition is caused by overuse of the forearm muscles, leading to pain on the inner side of the elbow.
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness on the inner side of the elbow
- Stiffness
- Weakness in the hands and wrists
Treatment:
- Rest
- Ice application
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Similar to golfer’s elbow, tennis elbow is caused by overuse, but it affects the outer side of the elbow.
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness on the outer side of the elbow
- Weak grip strength
- Pain when lifting or gripping objects
Treatment:
- Rest
- Ice application
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Physical therapy
- In severe cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery
Prevention Tips
To prevent arm injuries, consider the following measures:
- Warm up properly before physical activities
- Use proper techniques during sports and exercises
- Avoid repetitive motions that strain the arm muscles and tendons
- Use protective gear during high-risk activities
- Maintain overall physical fitness to support joint and muscle health
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the first steps to take after an arm injury?
Immediately after an arm injury, use the RICE method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Avoid using the injured arm and seek medical attention if the pain is severe or if there is significant swelling or deformity.
How long does it take for a sprain or strain to heal?
The healing time for a sprain or strain depends on the severity of the injury. Mild strains may heal within a few days, while severe sprains can take several weeks to months to fully recover.
When should I see a doctor for arm pain?
You should see a doctor if you experience severe pain, swelling, or deformity, or if you cannot move your arm. Also, seek medical attention if the pain persists despite home treatment.
Can arm injuries lead to long-term complications?
If not properly treated, arm injuries can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and weakness. Early and appropriate treatment is crucial to prevent long-term complications.
How can I strengthen my arms to prevent injuries?
Regular strength training exercises, such as weightlifting and resistance band workouts, can help strengthen the arm muscles and joints. Always use proper techniques and gradually increase the intensity of your workouts.